Sydney University Media Release, 20 October 2025
Plate tectonics played central role shaping life-supporting oceans
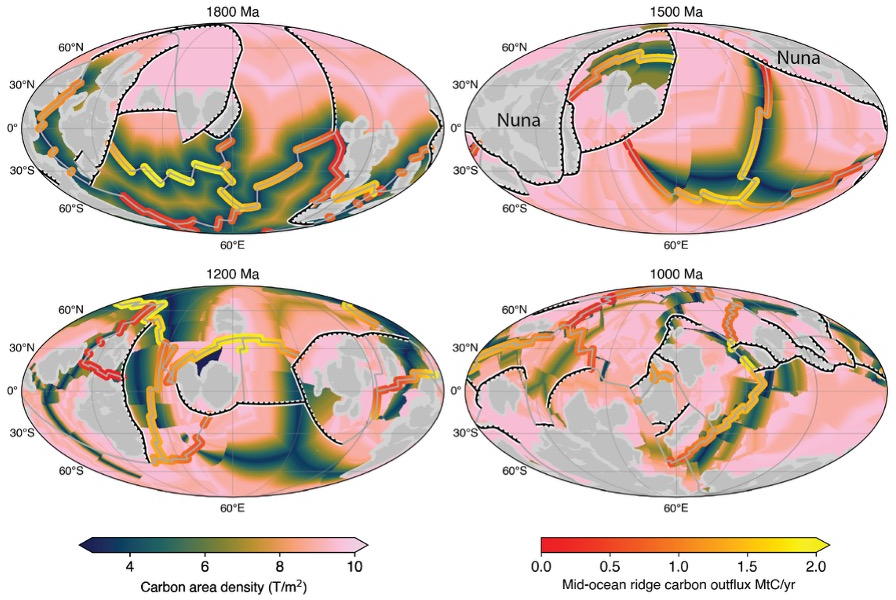
Between 1.8 and 0.8 billion years ago, Earth’s tectonic activity locked atmospheric carbon dioxide into carbonate minerals within the oceanic crust, paving the way for oxygen-rich seas and evolving life. Source: research paper
A study led by researchers from the University of Sydney and the University of Adelaide has revealed the breakup of an ancient supercontinent about 1.5 billion years ago transformed Earth’s surface environments, paving the way for the emergence of complex life.
The research, published in Earth and Planetary Science Letters, challenges the notion of the “Boring Billion” – a time of supposed stasis in Earth’s history – and shows that plate tectonics was reshaping the planet, triggering the conditions that supported oxygen-rich oceans and the appearance of the first eukaryotes, the ancestors of all complex life.
“Our work reveals that deep Earth processes, specifically the breakup of the ancient supercontinent Nuna, set off a chain of events that reduced volcanic carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions and expanded the shallow marine habitats where early eukaryotes evolved,” said Professor Dietmar Müller, from the EarthByte Group at the University of Sydney and lead author of the study.
A dynamic Earth beneath a ‘boring’ surface
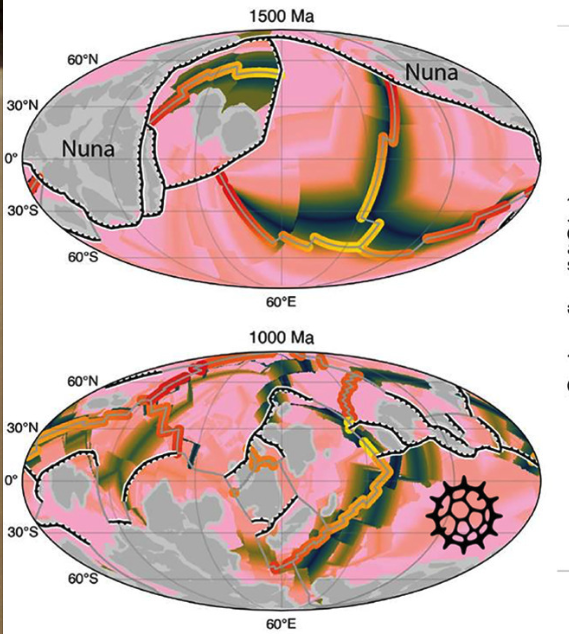
Between 1.8 and 0.8 billion years ago, Earth’s continents assembled and broke apart twice, first forming Nuna, then Rodinia. Using a new plate tectonic model covering 1.8 billion years of Earth’s history, the team reconstructed changes in plate boundaries, continental margins, and carbon exchange between the mantle, oceans, and atmosphere.
They discovered that as Nuna fragmented around 1.46 billion years ago, the total length of shallow continental shelves more than doubled to about 130,000 kilometres. These shallow-water environments likely hosted extensive oxygenated and temperate seas, providing long-lived, stable environments for complex life to flourish.
At the same time volcanic outgassing of CO2 decreased, while the storage of carbon in the ocean crust increased due to an expansion of mid-ocean ridge flanks. Here seawater seeps into cracks in the crust, is heated and the CO2 it contains is stripped out to produce limestone.
“This dual effect – reduced volcanic carbon release and enhanced geological carbon storage – cooled Earth’s climate and altered ocean chemistry, creating conditions suitable for the evolution of more complex life,” said co-author Associate Professor Adriana Dutkiewicz, also from the School of Geosciences at the University of Sydney.
From tectonics to life
The study’s results indicate that the appearance of the first fossil eukaryotes about 1.05 billion years ago coincided with continental dispersal and expanded shallow seas.
“We think these vast continental shelves and shallow seas were crucial ecological incubators,” said Associate Professor Juraj Farkaš from the University of Adelaide. “They provided tectonically and geochemically stable marine environments with presumably elevated levels of nutrients and oxygen, which in turn were critical for more complex lifeforms to evolve and diversify on our planet.”
The findings link deep-Earth dynamics with near-surface geochemical and biological evolution, offering a unifying framework that connects plate tectonics, the global carbon cycle, ocean chemistry and the emergence of complex life.
A new framework for Earth’s evolution
This research represents the first time that deep-time plate tectonic reconstructions have been quantitatively linked to long-term carbon outgassing and biological milestones over nearly two billion years. The authors used computational models combining tectonic reconstructions with thermodynamic simulations of carbon storage and degassing through subduction and volcanism.
“Our approach shows how plate tectonics has helped shape the habitability of the Earth,” Professor Müller said. “It provides a new way to think about how tectonics, climate, and life co-evolved through deep time.”
DOWNLOAD a copy of the research and images of Professor Müller and Associate Professor Dutkiewicz at this link.
VIDEO of the tectonic plates moving from 1.8 billion years ago to present available here.
MEDIA ENQUIRIES
Marcus Strom | marcus.strom@sydney.edu.au | +61 474 269 459
RESEARCH
Workflow data and code are publicly available at this link.
![]()