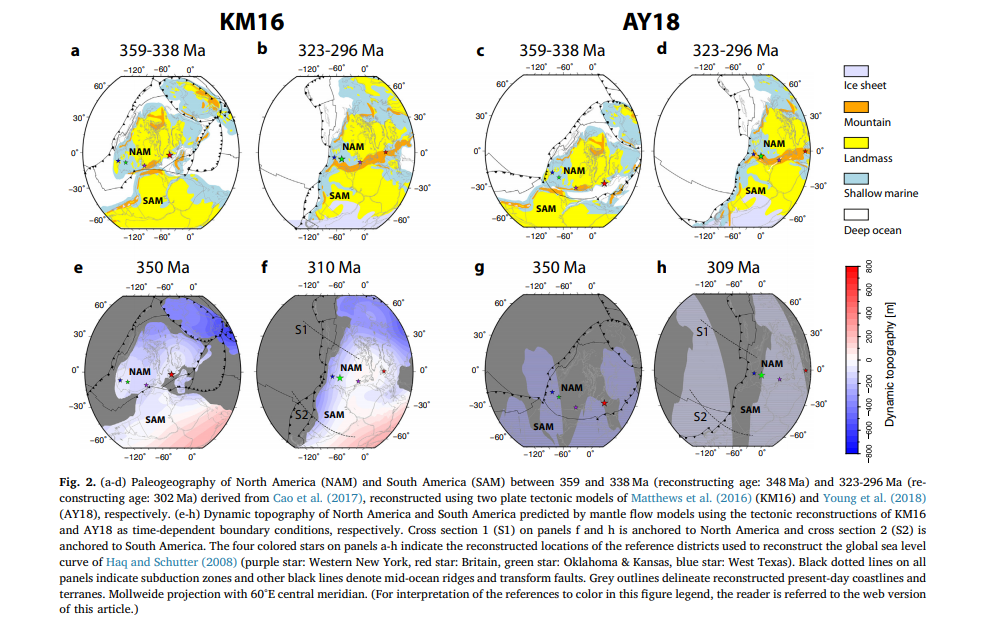
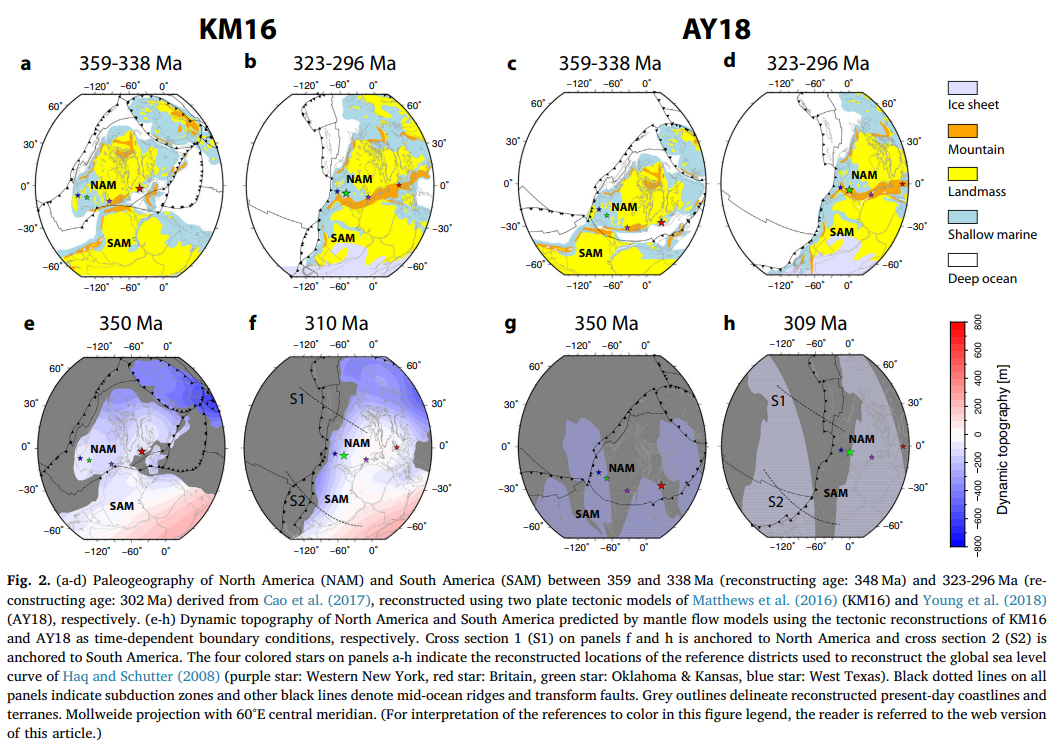
 Citation
Citation
Flament, N., Gurnis, M., Williams, S., Seton, M., Skogseid, J., Heine, C., & Müller, R. D. (2014). Topographic asymmetry of the South Atlantic from global models of mantle flow and lithospheric stretching. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 387, 107-119. dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2013.11.017.
Abstract
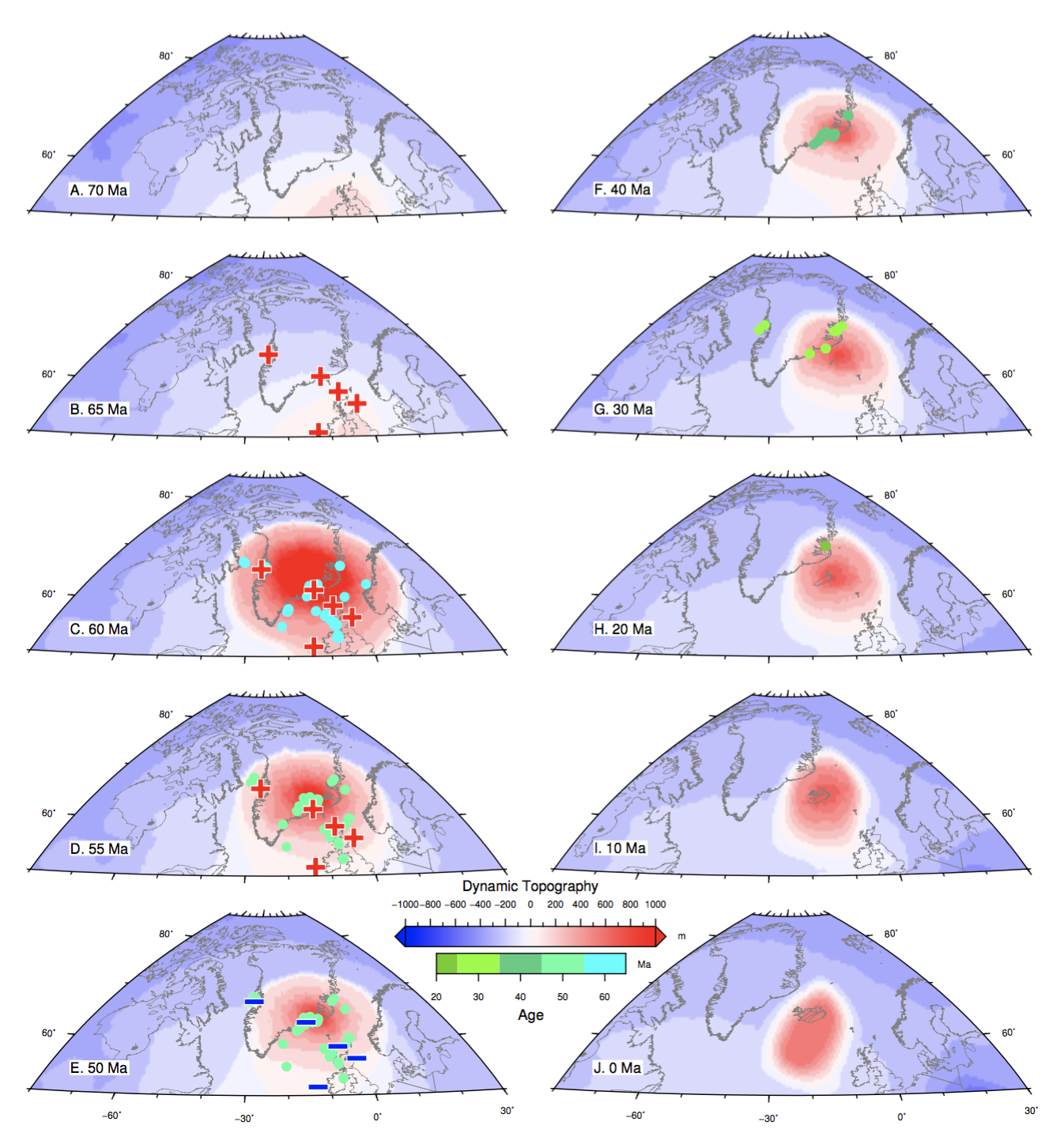
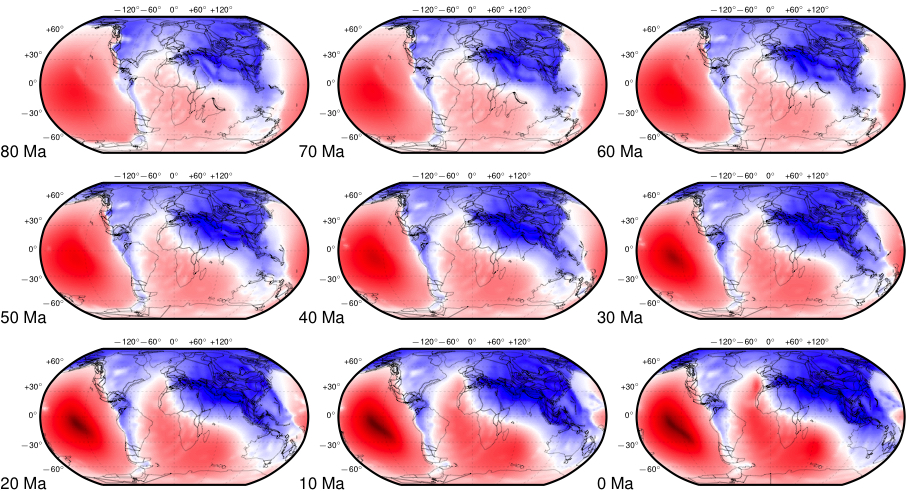
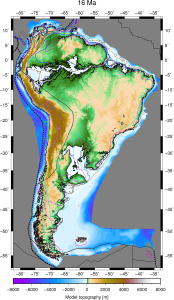
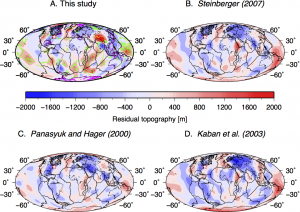
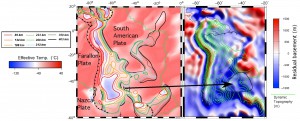
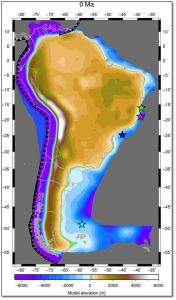
The relief of the South Atlantic is characterized by elevated passive continental margins along southern Africa and eastern Brazil, and by the bathymetric asymmetry of the southern oceanic basin where the western flank is much deeper than the eastern flank. We investigate the origin of these topographic features in the present and over time since the Jurassic with a model of global mantle flow and lithospheric deformation. The model progressively assimilates plate kinematics, plate boundaries and lithospheric age derived from global tectonic reconstructions with deforming plates, and predicts the evolution of mantle temperature, continental crustal thickness, long-wavelength dynamic topography, and isostatic topography. … Read more…