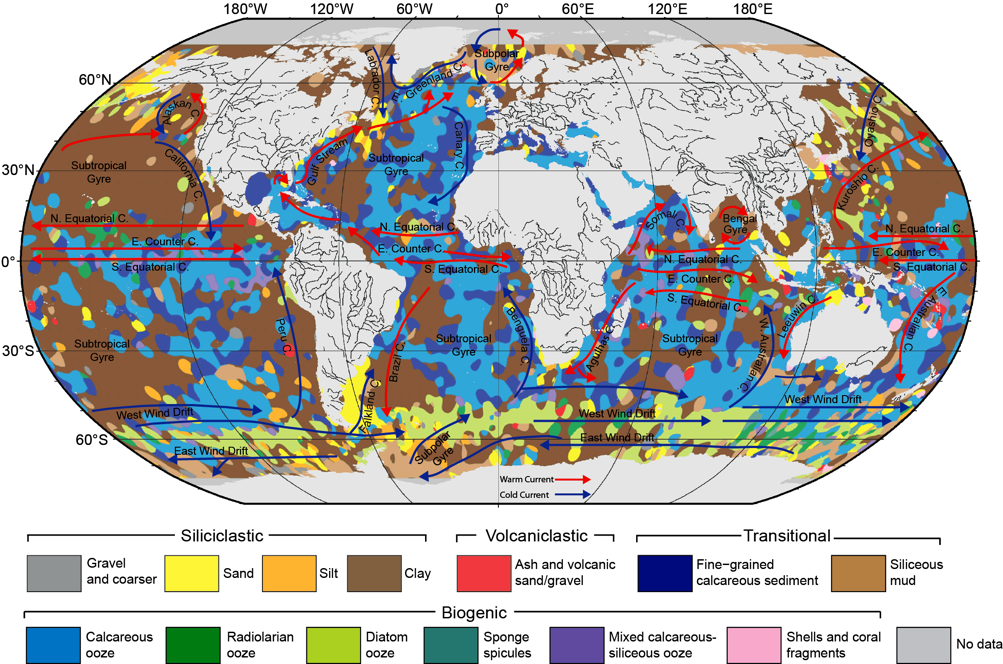
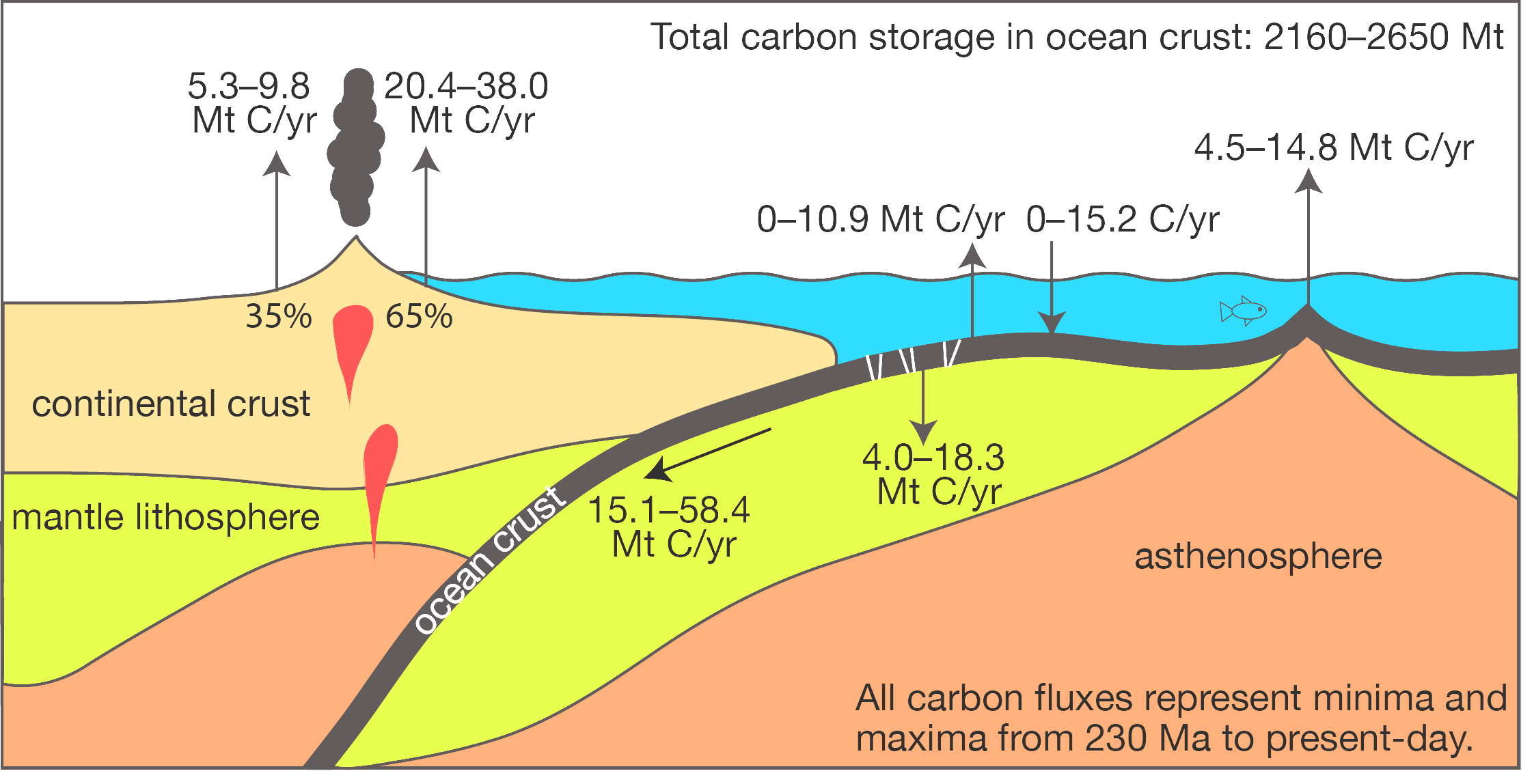
 When organic particles sink from the surface ocean to the seafloor, a small but significant proportion of atmospheric carbon is stored away. Adriana Dutkiewicz and colleagues at the University of Sydney and Data61/CSIRO have now used global data sets collected over decades combined with cutting-edge big data analysis to understand how this process depends on surface ocean environments. … Read more…
When organic particles sink from the surface ocean to the seafloor, a small but significant proportion of atmospheric carbon is stored away. Adriana Dutkiewicz and colleagues at the University of Sydney and Data61/CSIRO have now used global data sets collected over decades combined with cutting-edge big data analysis to understand how this process depends on surface ocean environments. … Read more…
Mars attracts: how Earth’s planetary interactions drive deep-sea circulation
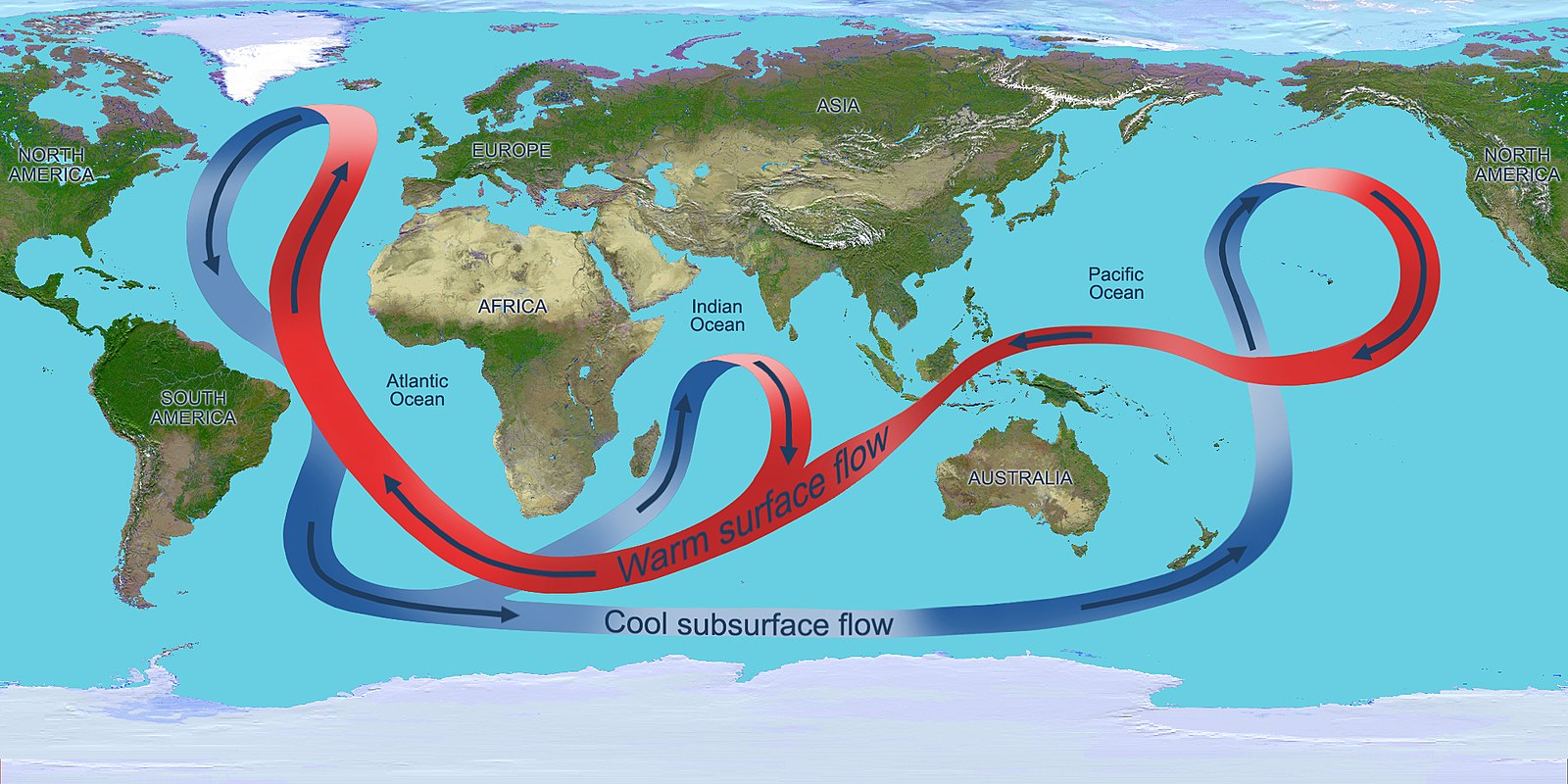
12 March 2024, The University of Sydney Media Release Giant whirlpools in warming oceans could mitigate Gulf Stream stagnation Geoscientists at Sydney and Sorbonne have identified a 2.4-million-year cycle in the geological record that show the energy of deep-sea currents wax and wane as oceans cool and warm. Earth’s distance to Mars varies between 55 … Read more…
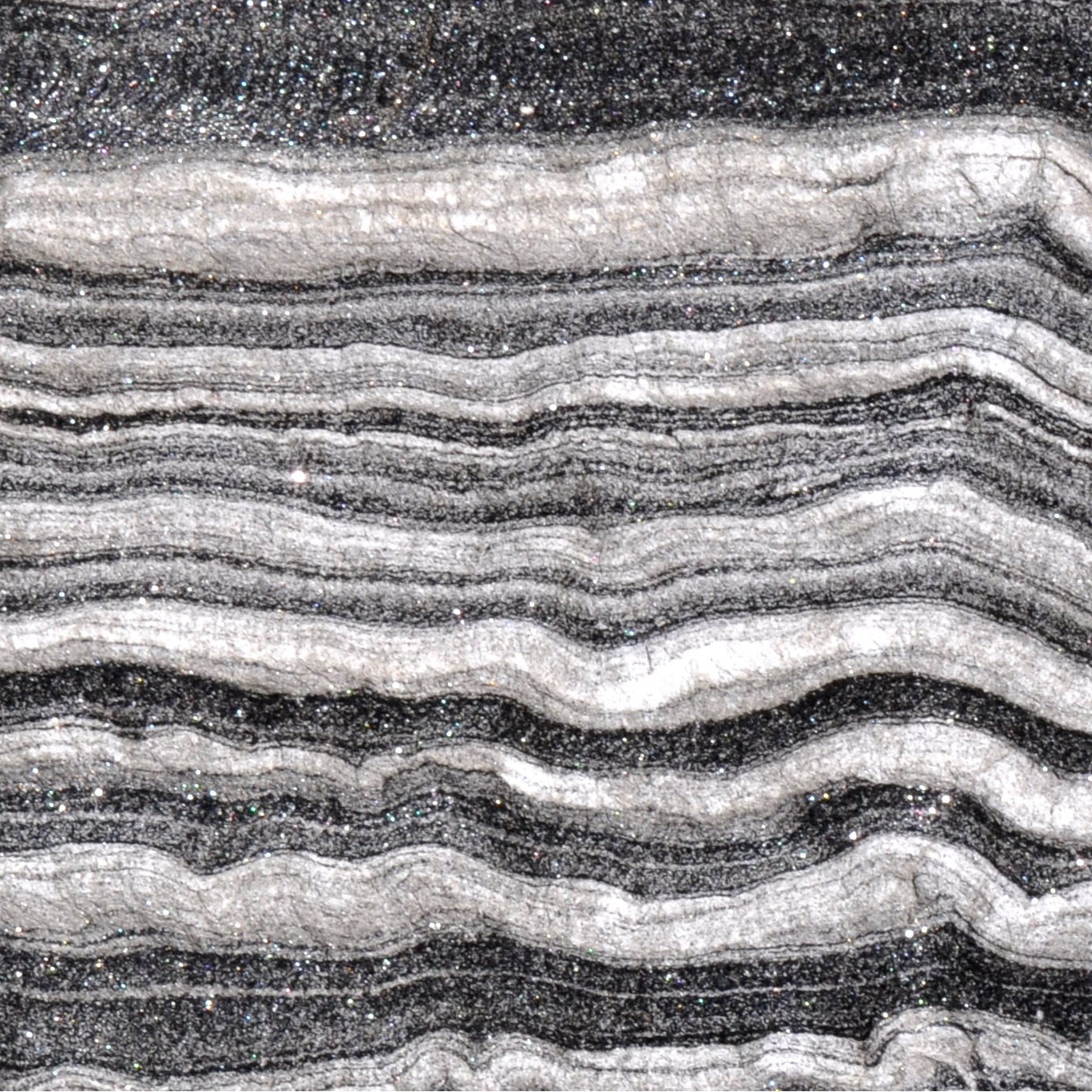
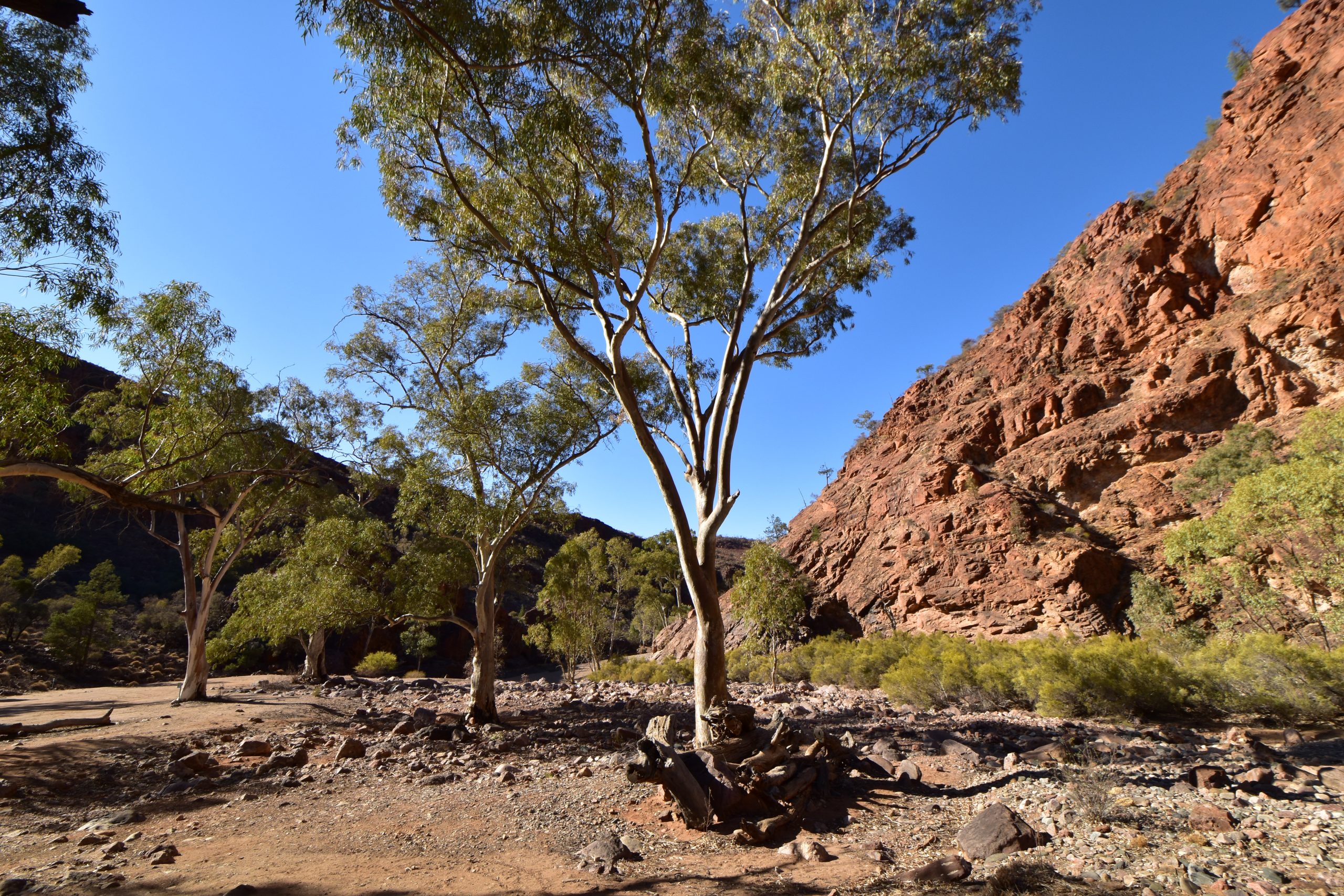





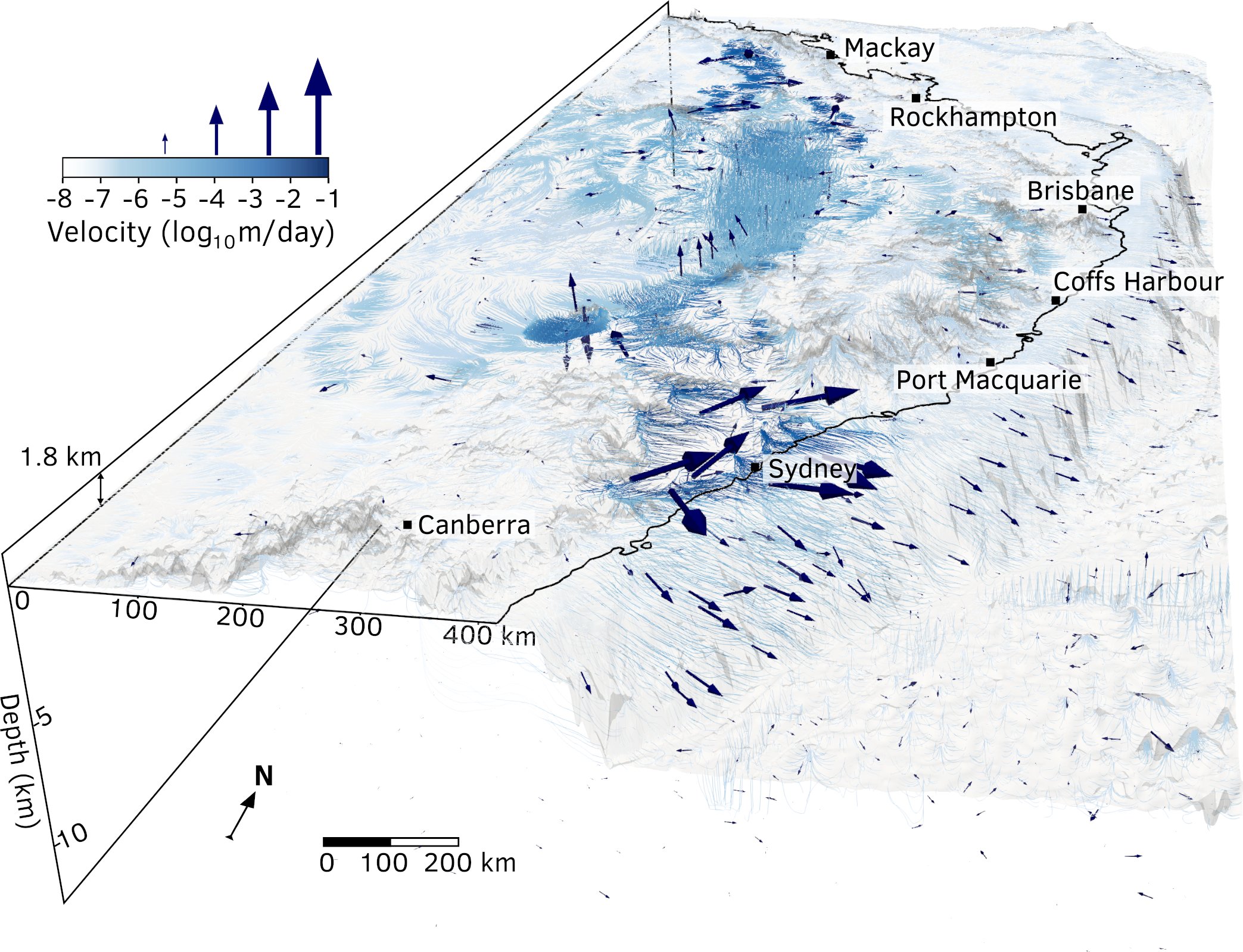



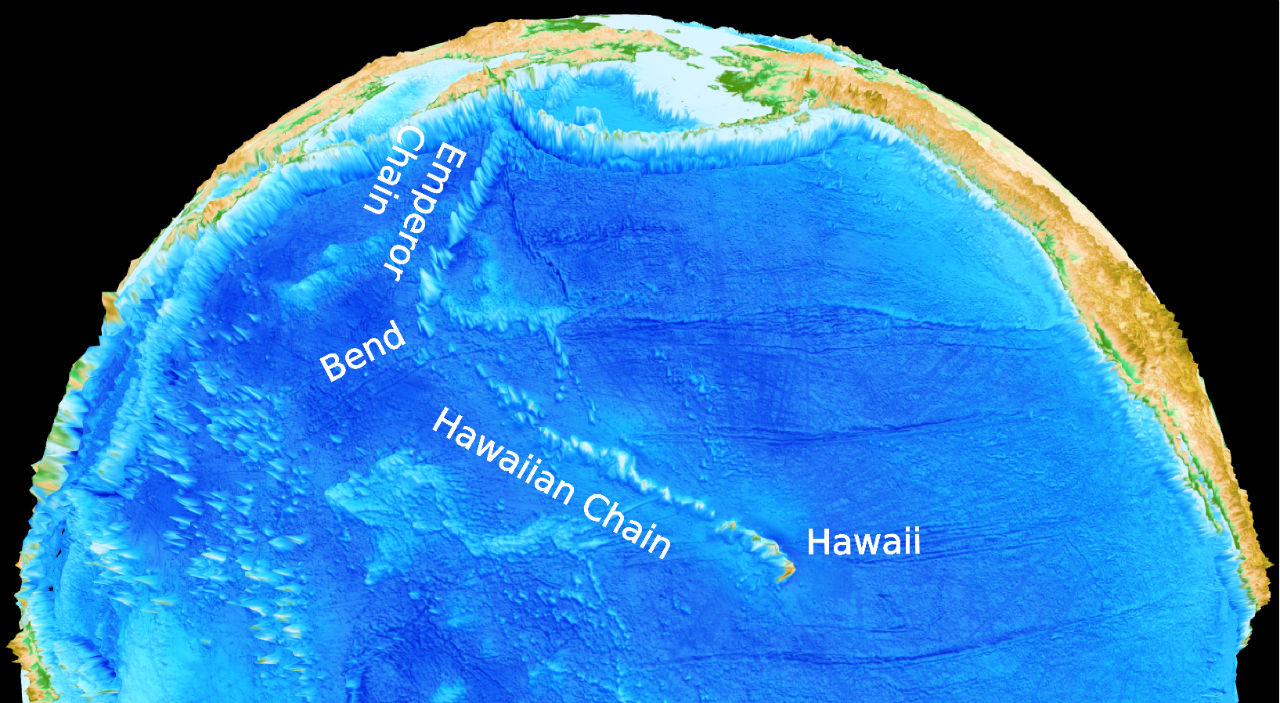
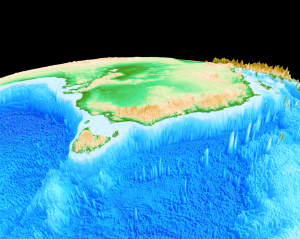 Geologists from the University of Sydney and the California Institute of Technology have solved the mystery of how Australia’s highest mountain – Mount Kosciusko – and surrounding alps came to exist.
Geologists from the University of Sydney and the California Institute of Technology have solved the mystery of how Australia’s highest mountain – Mount Kosciusko – and surrounding alps came to exist.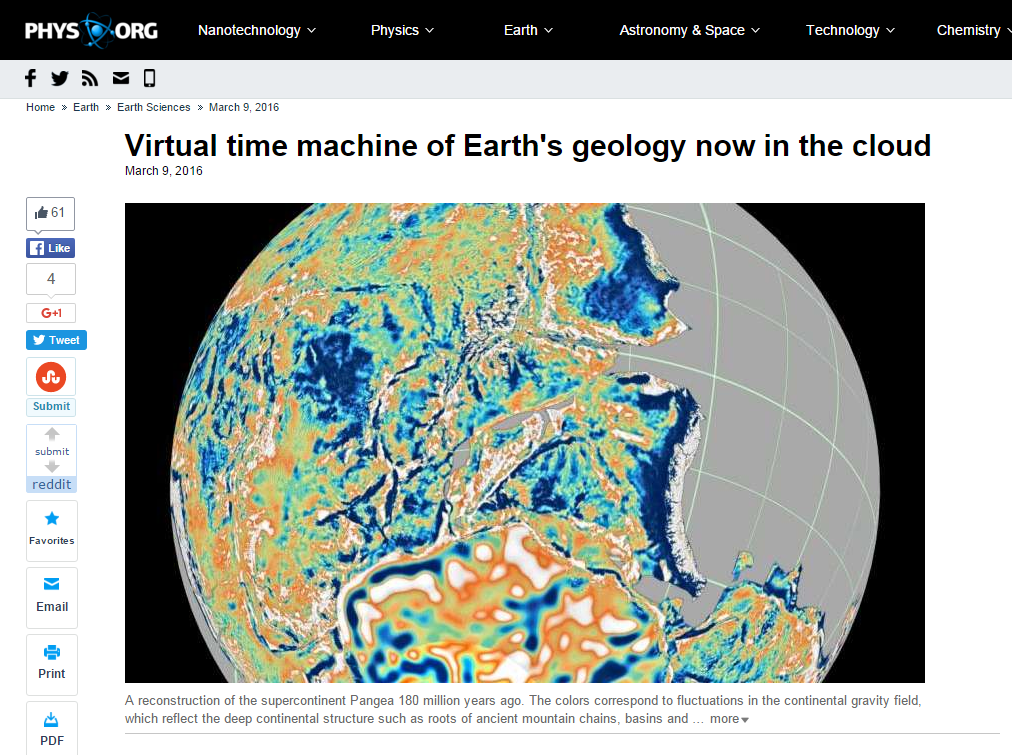
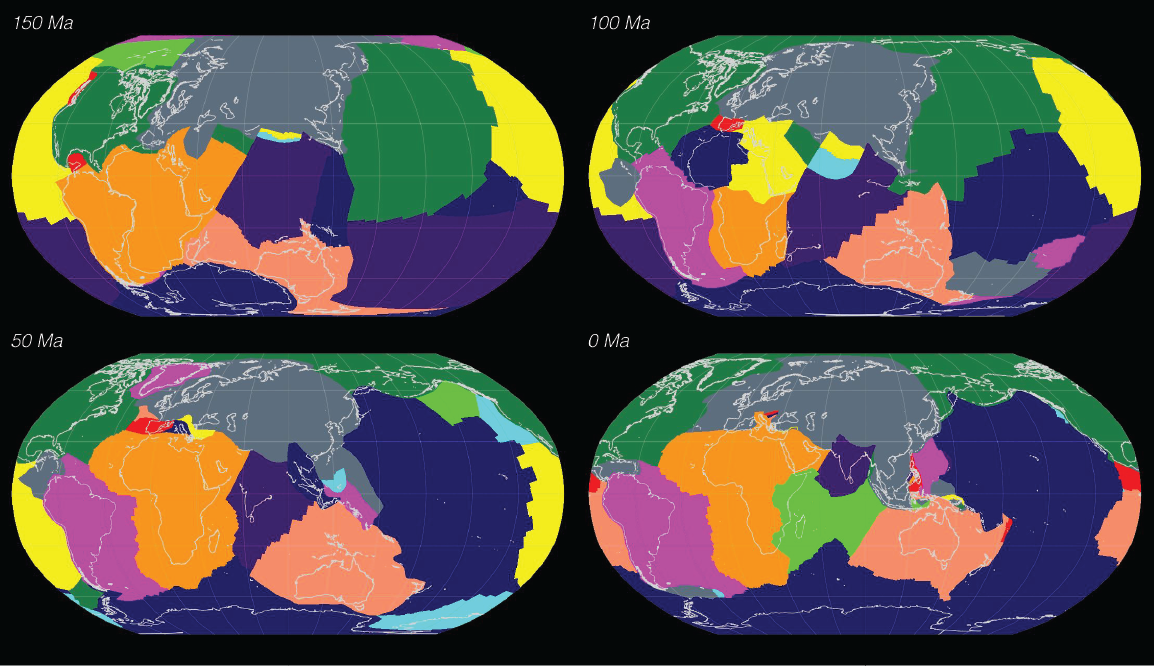
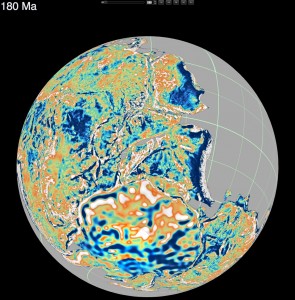 How did Madagascar once slot next to India? Where was Australia a billion years ago?
How did Madagascar once slot next to India? Where was Australia a billion years ago?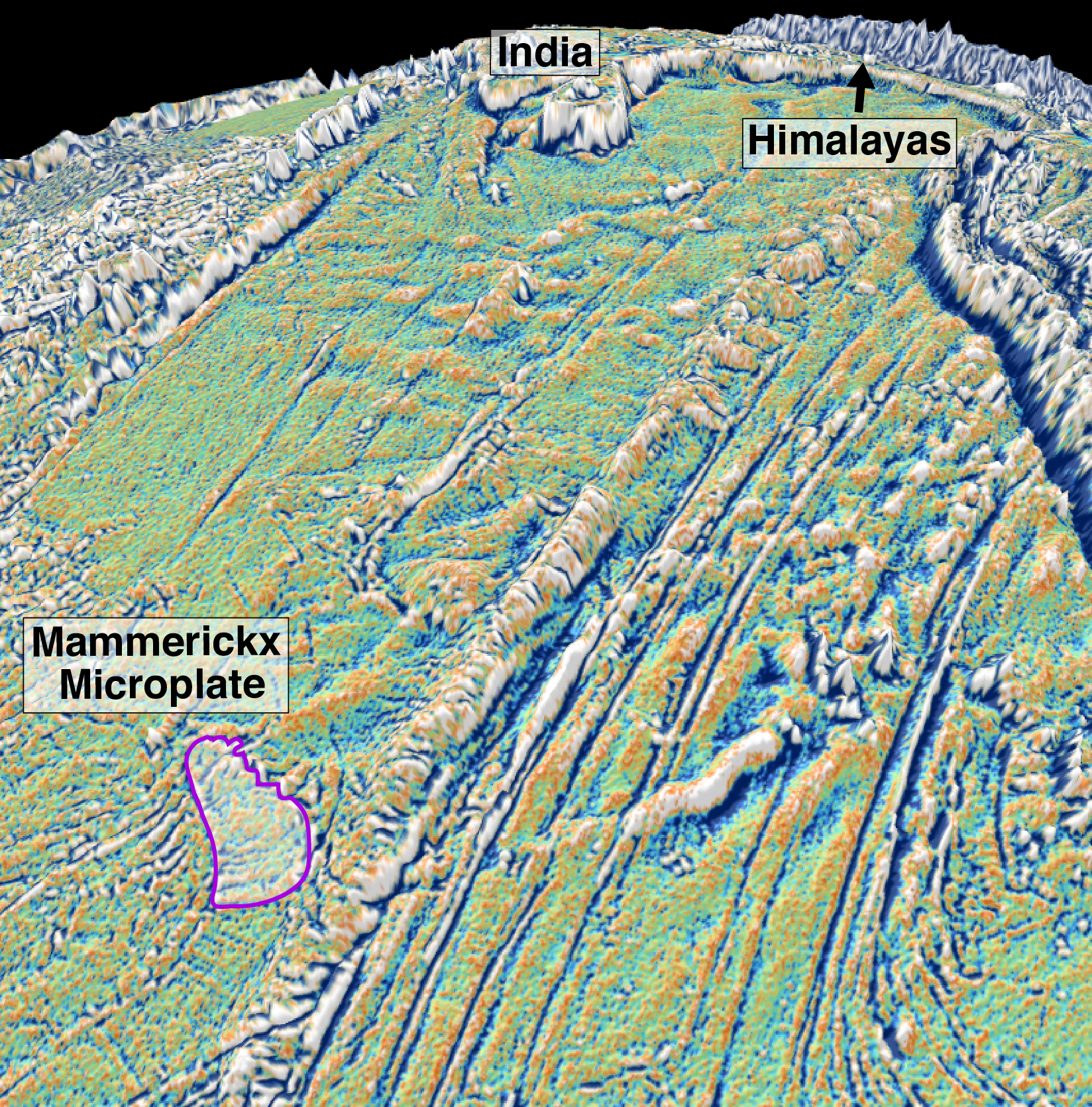
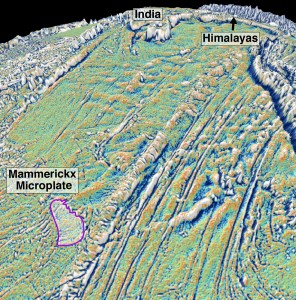
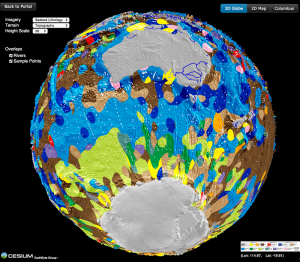 New digital seafloor geology map uses artificial intelligence and big data to boost understanding of the ocean floor
New digital seafloor geology map uses artificial intelligence and big data to boost understanding of the ocean floor