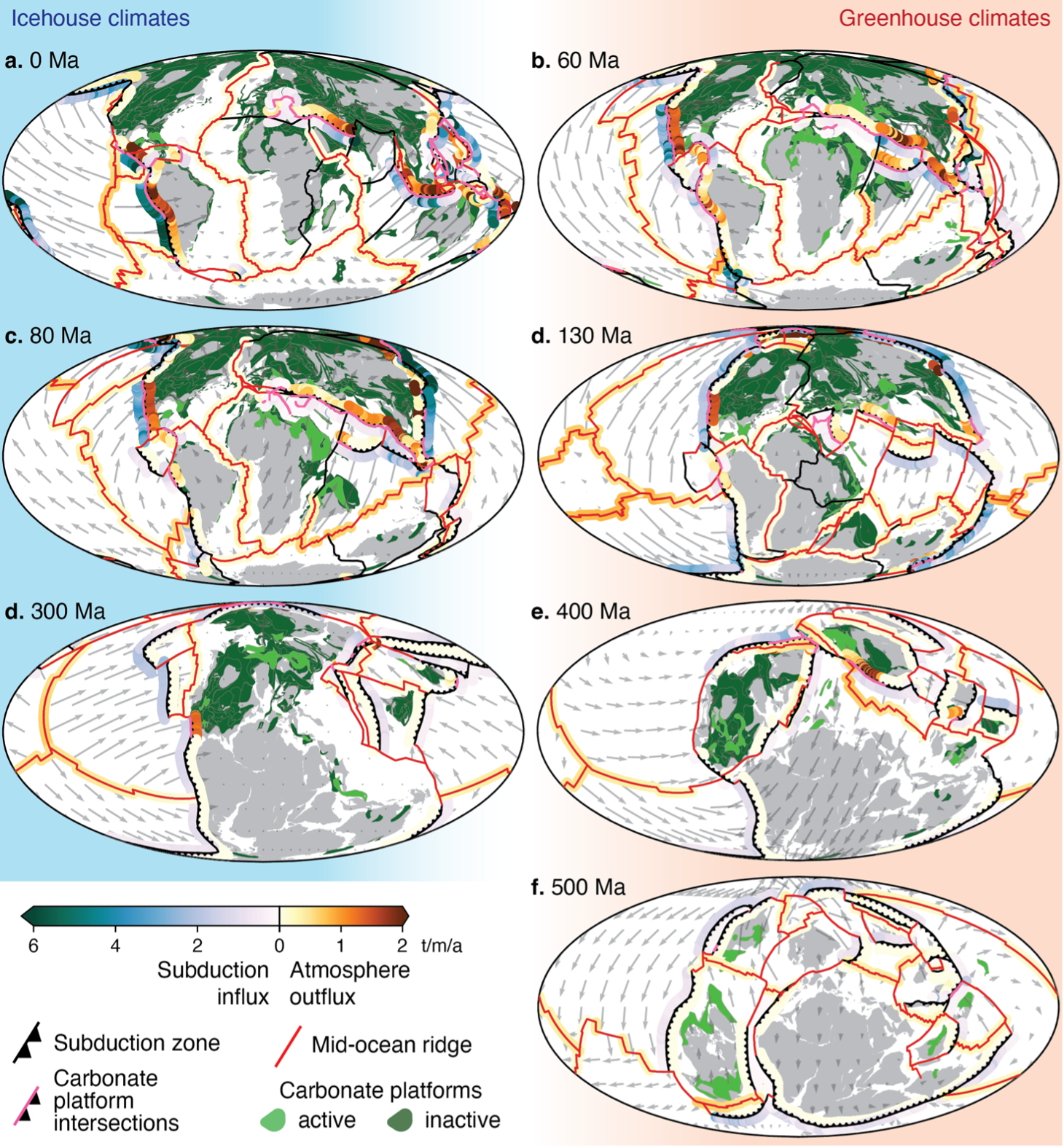
Carbon emissions along divergent plate boundaries modulate icehouse-greenhouse climates
The exchange of carbon between oceanic plates, the deep Earth, and the atmosphere plays a significant role in modulating global climate1,2. Icehouse-greenhouse climate fluctuations have been attributed to changes in palaeogeography and solid Earth degassing3, particularly along continental arcs2,4,5, to arc weathering5 and to the sequestration of carbon into oceanic carbonate-rich sediments6. However, the proportions … Read more…