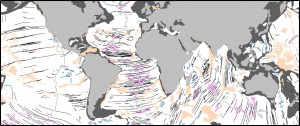
 We present a global community data set of fracture zones (FZs), discordant zones, propagating ridges, V-shaped structures and extinct ridges, digitized from vertical gravity gradient (VGG) maps.
We present a global community data set of fracture zones (FZs), discordant zones, propagating ridges, V-shaped structures and extinct ridges, digitized from vertical gravity gradient (VGG) maps.
… Read more…
Kara Matthews is awarded the Chris Powell Medal
Congratulations to Kara Matthews who has been awarded the prestigious Chris Powell Medal for Postgraduate Research in Tectonics and Structural Geology from the Geological Society of Australia. She was presented her medal at a meeting of the Specialist Group in Tectonics & Structural Geology in Waratah Bay, Victoria. Well done Kara! Download the paper – … Read more…
