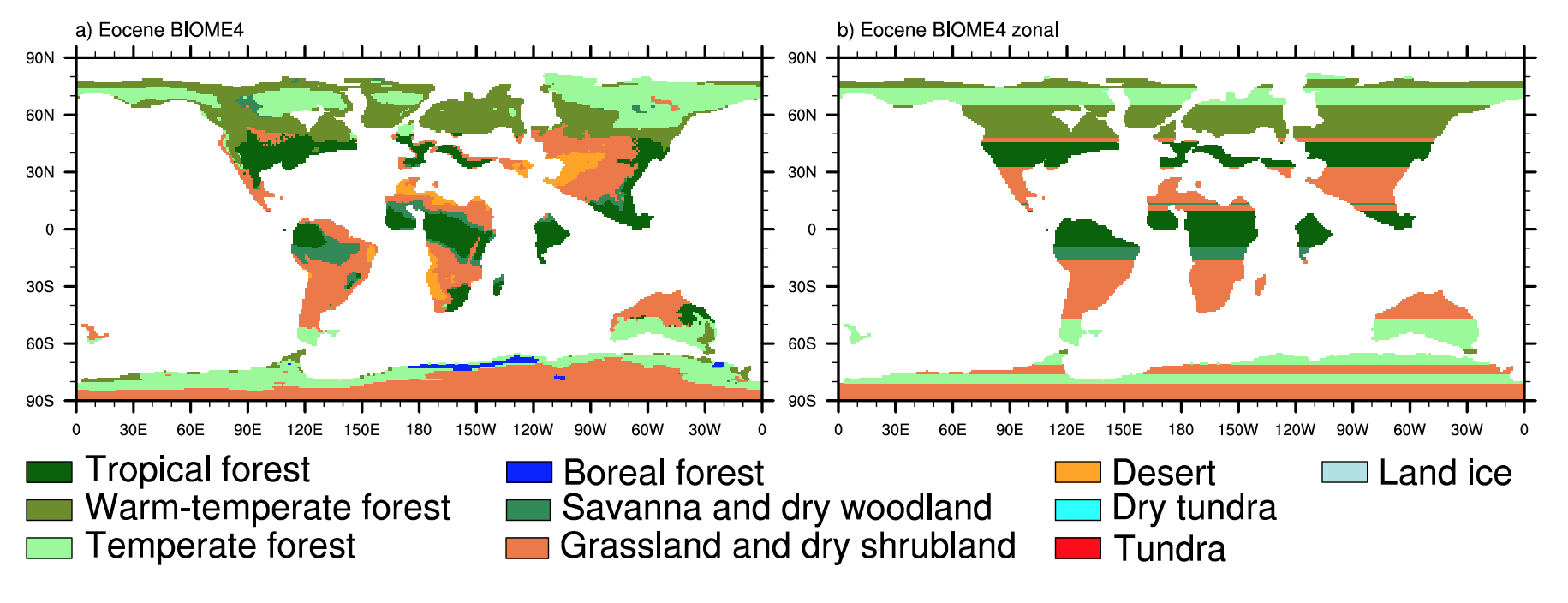
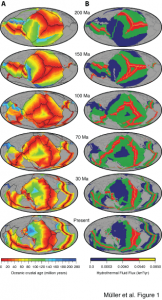
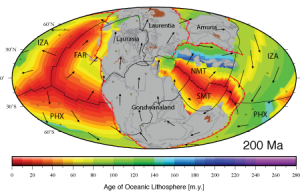
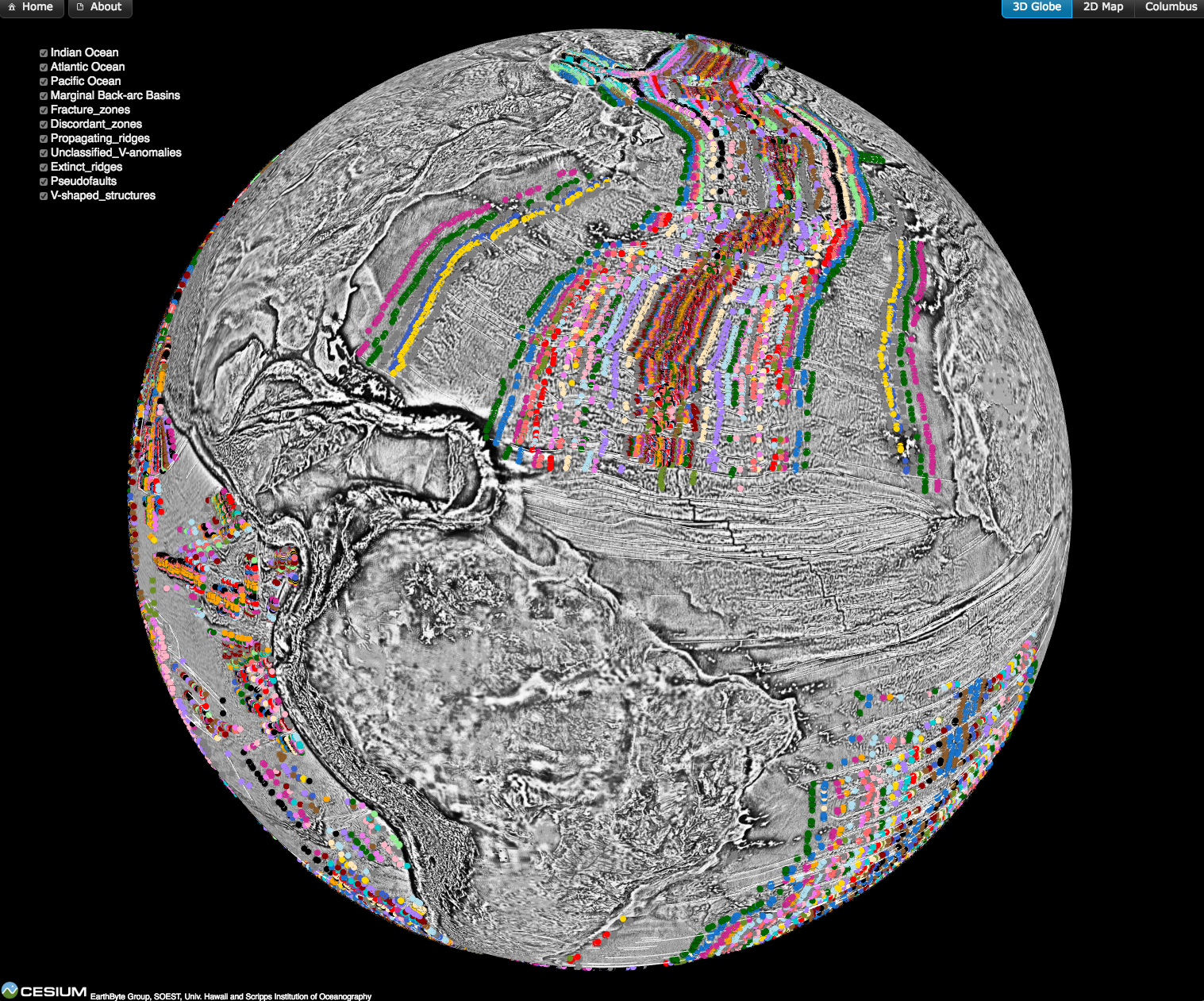
 Magnetic anomaly identifications form the primary data set from which the age of the oceanic lithosphere can be determined, a critical component of reconstructing the seafloor spreading history of ocean basins. This data is now available as part of an open source, community-driven online repository that contains quality-checked magnetic anomaly picks, organised by ocean basin and publication source.
Magnetic anomaly identifications form the primary data set from which the age of the oceanic lithosphere can be determined, a critical component of reconstructing the seafloor spreading history of ocean basins. This data is now available as part of an open source, community-driven online repository that contains quality-checked magnetic anomaly picks, organised by ocean basin and publication source.
Plate reconstructions of Southeast Asia
This animation is from our recent work on Southeast Asian plate reconstructions.Read the peer-reviewed paperCitationZahirovic, S., M. Seton, and R. Müller (2014), The Cretaceous and Cenozoic tectonic evolution of Southeast Asia, Solid Earth (EGU), 5, 227-273. doi: 10.5194/se-5-227-2014.View similar animations on our EarthByte YouTube channel