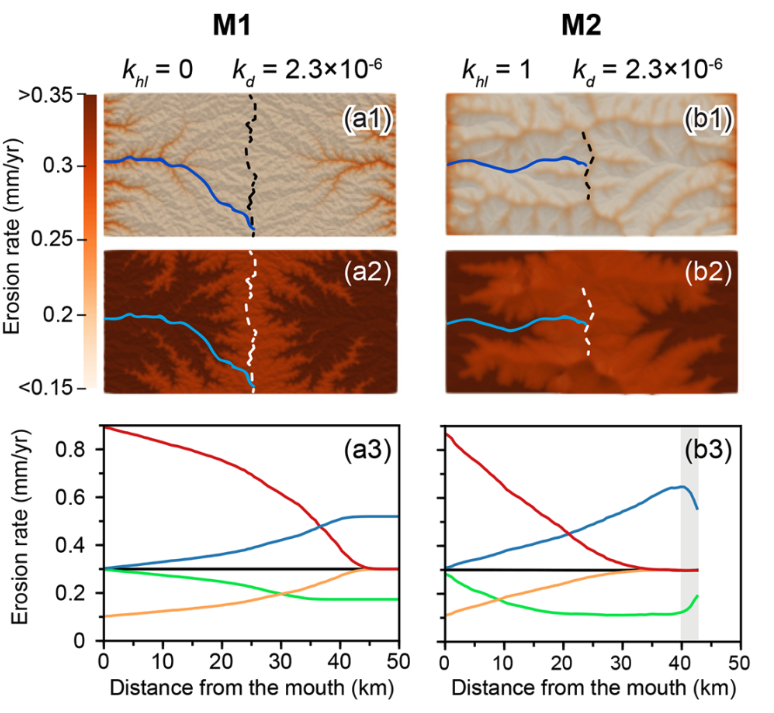
Rainfall and tectonic forcing lead to contrasting headwater slope evolutions
Landscapes evolve through the coupled effects of tectonics and surface processes. Previous studies have shown that uplift rate changes generate upstream-migrating erosion waves, altering downstream slopes while upstream slopes remain constant until the wave arrives. However, the distinctive differences between landscape responses to uplift versus climatic changes, particularly rainfall rate changes, remain incompletely described. This … Read more…