Mars attracts: how Earth’s planetary interactions drive deep-sea circulation
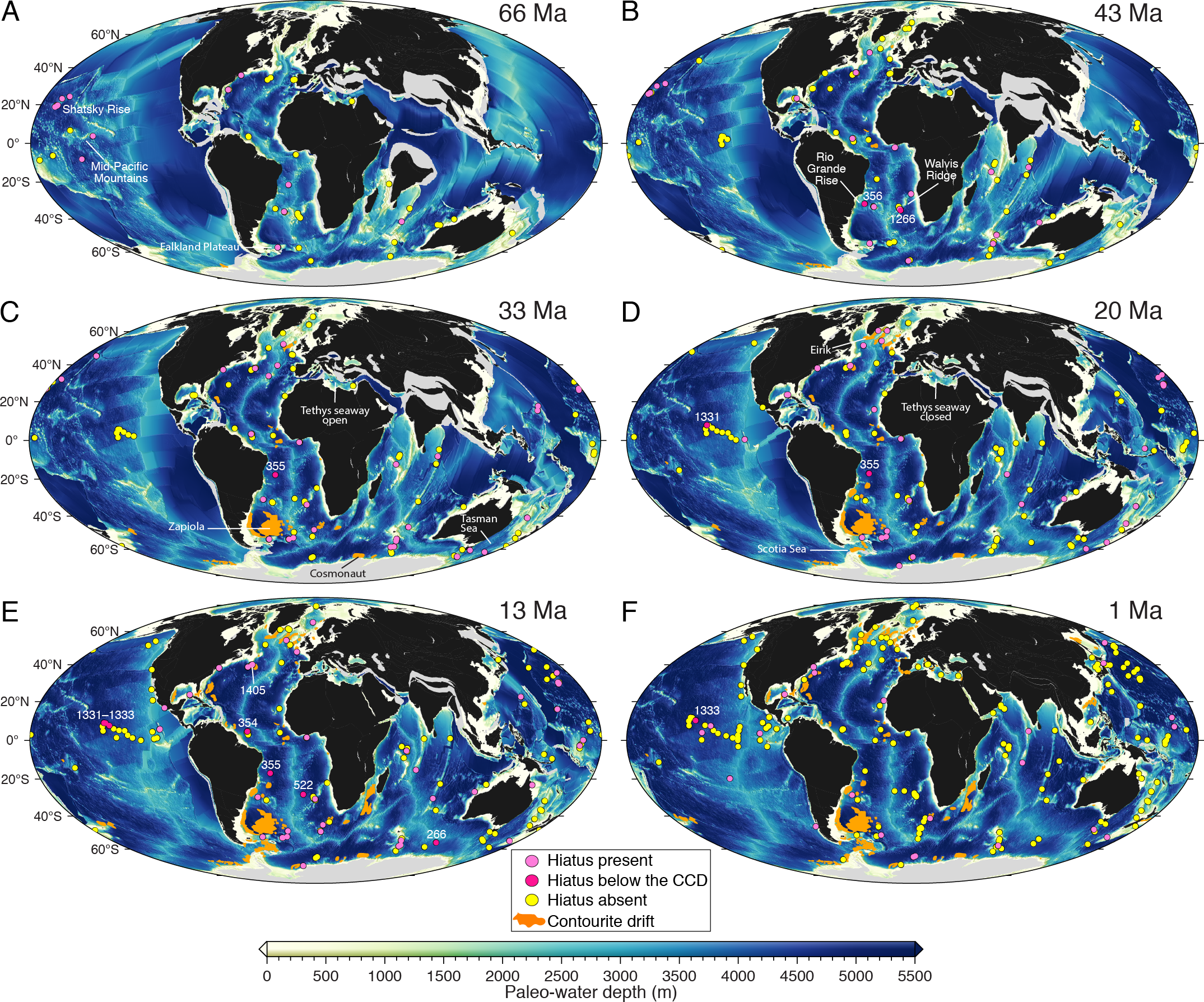
12 March 2024, The University of Sydney Media Release Giant whirlpools in warming oceans could mitigate Gulf Stream stagnation Geoscientists at Sydney and Sorbonne have identified a 2.4-million-year cycle in the geological record that show the energy of deep-sea currents wax and wane as oceans cool and warm. Earth’s distance to Mars varies between 55 … Read more…