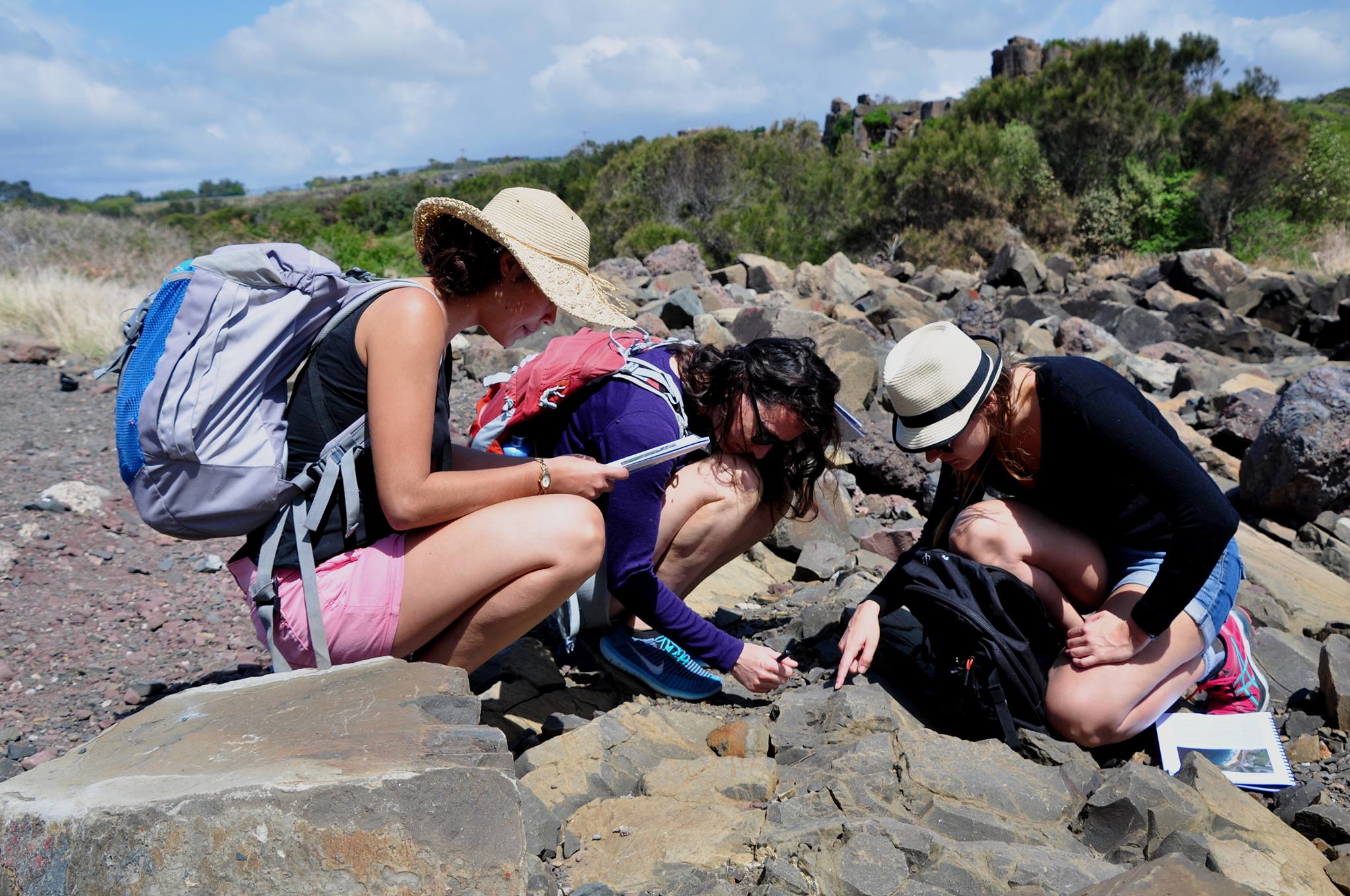
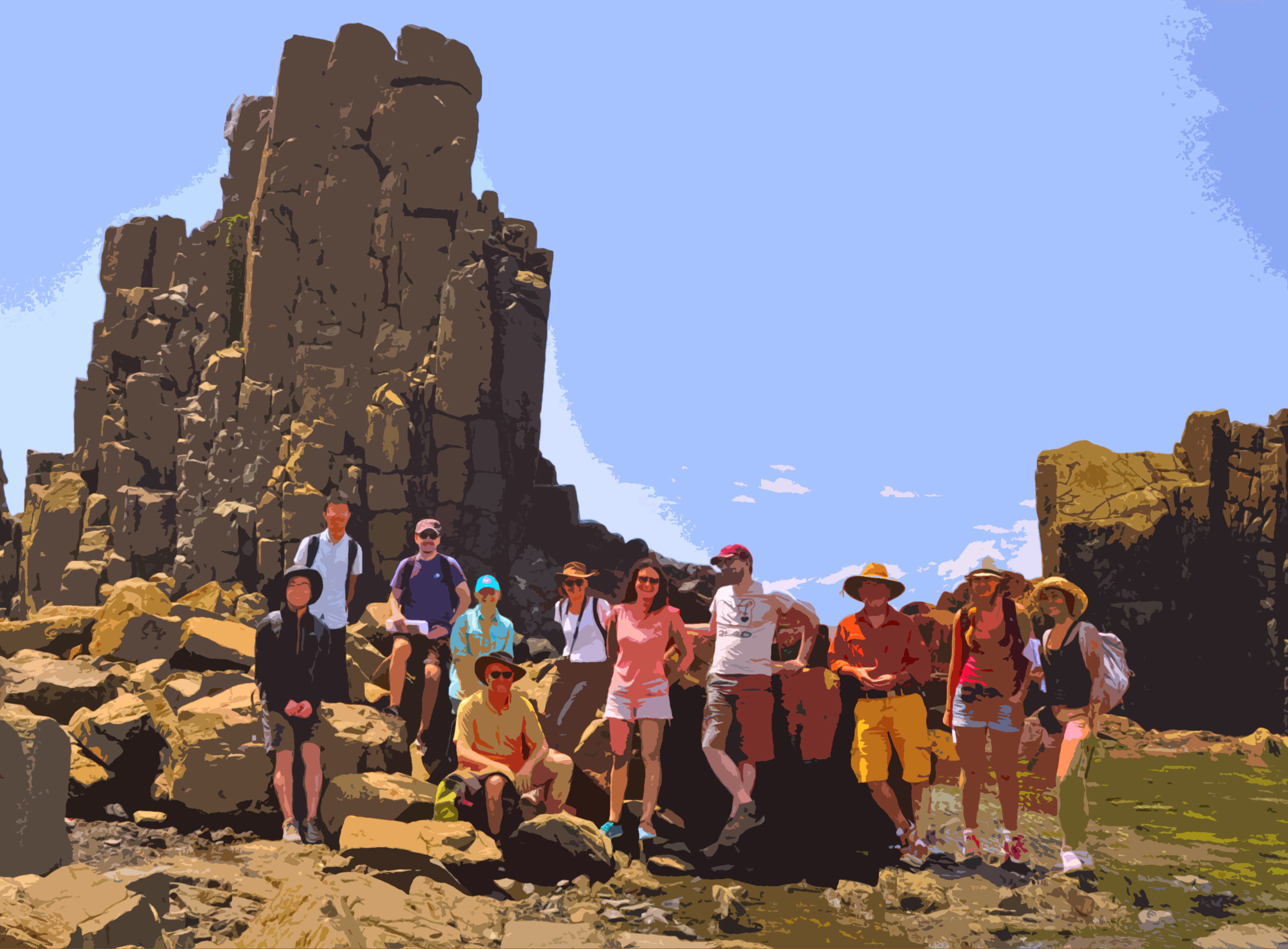
 The collaboration between the EarthByters at the School of Geosciences, University of Sydney and the Lyon-based Augury geodynamics group, who are currently visiting Sydney, led to a field trip to the Late Permian-Early Triassic Sydney Basin succession, beautifully exposed along the coastal Illawarra region. … Read more…
The collaboration between the EarthByters at the School of Geosciences, University of Sydney and the Lyon-based Augury geodynamics group, who are currently visiting Sydney, led to a field trip to the Late Permian-Early Triassic Sydney Basin succession, beautifully exposed along the coastal Illawarra region. … Read more…
Summer Scholarship Students 2017
EarthByte welcomes Summer Scholarship Students Madison East and Louis Johansson.








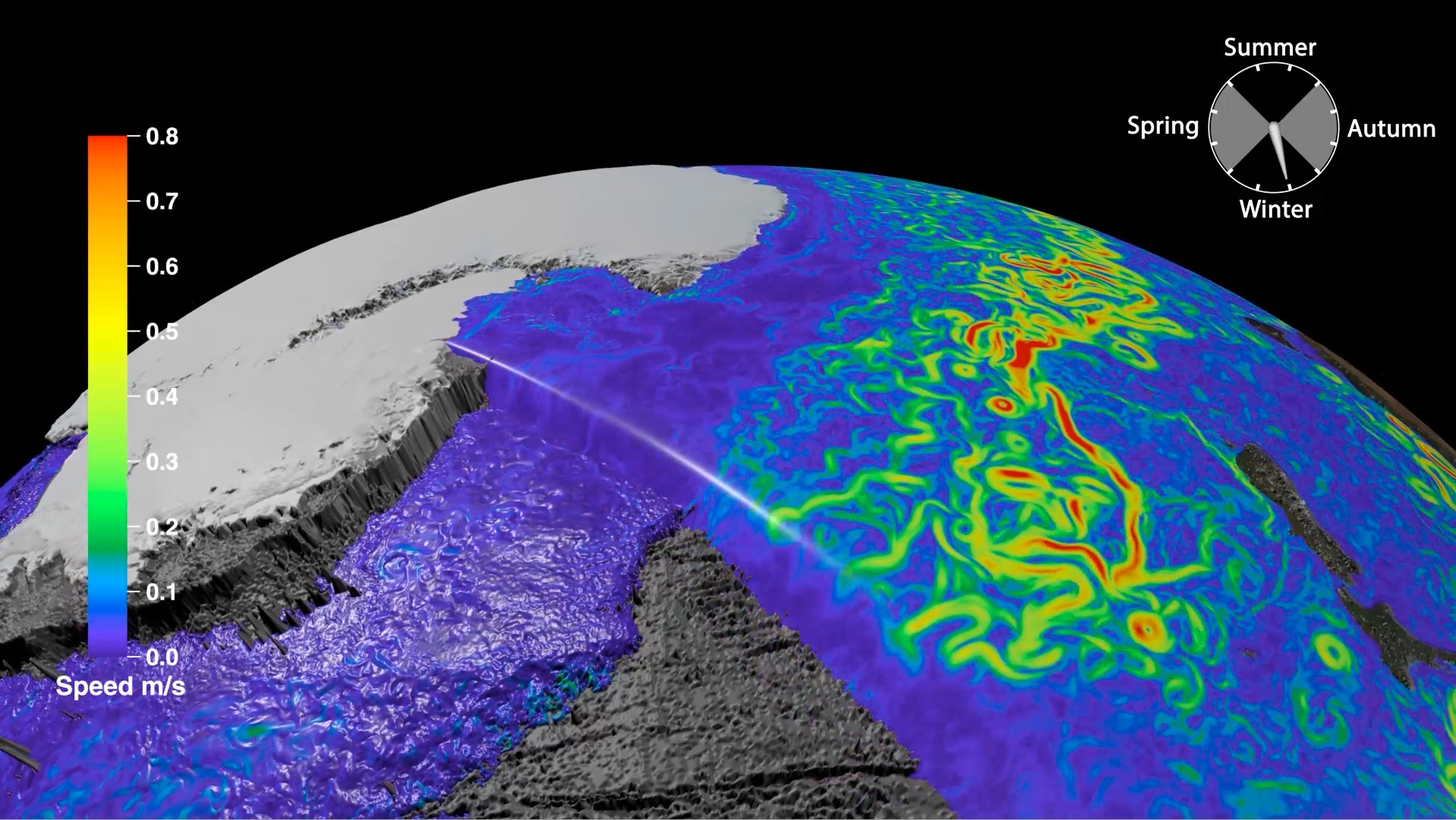
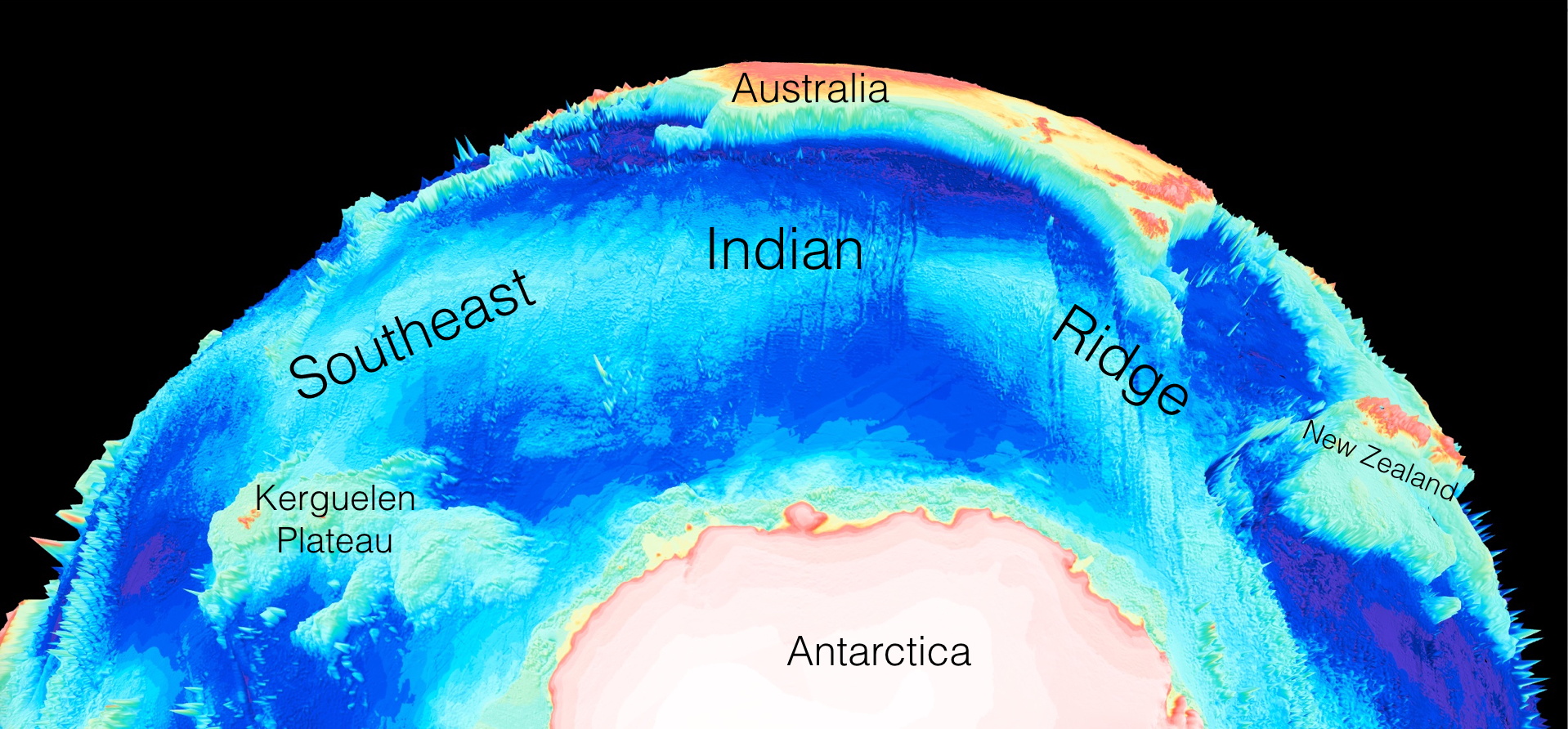
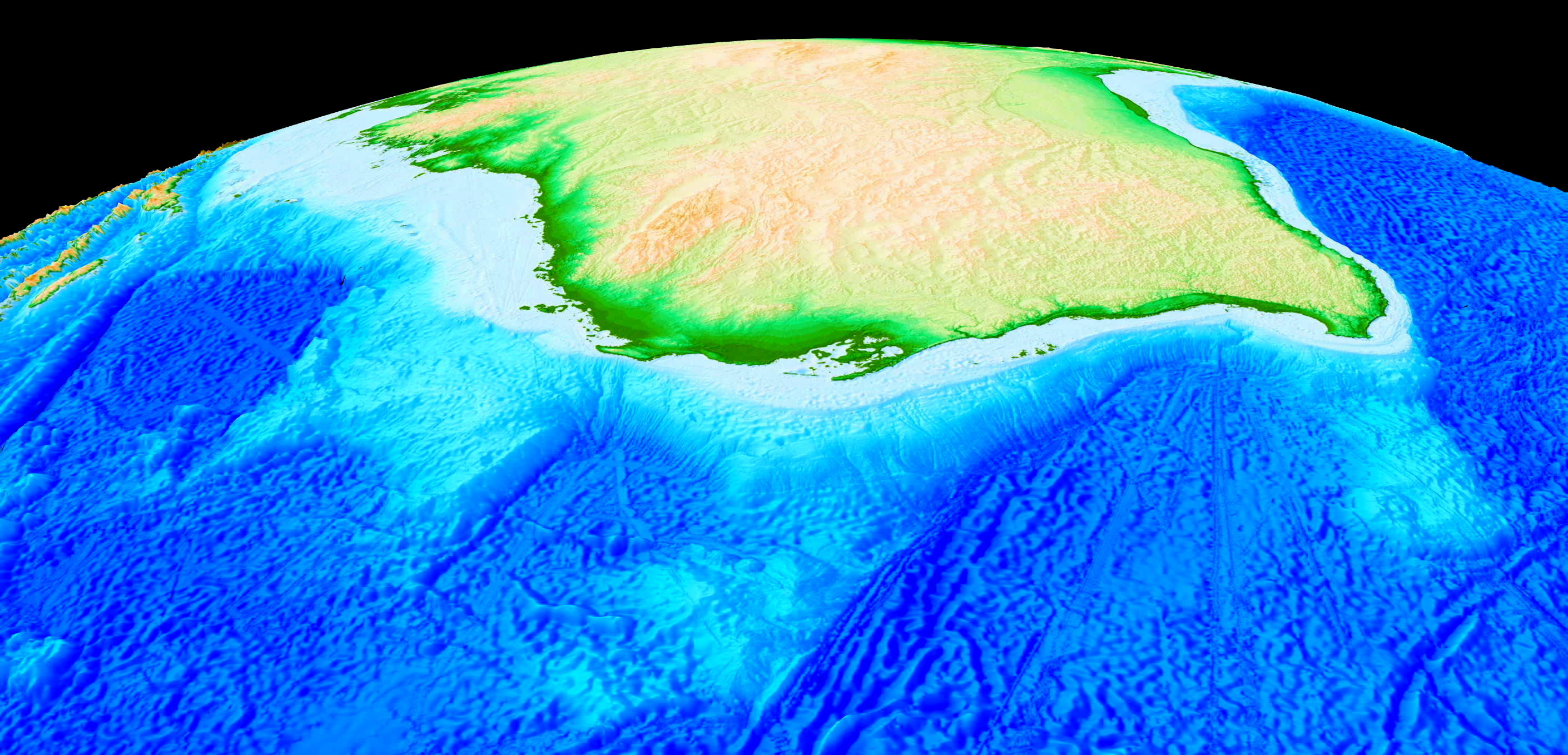


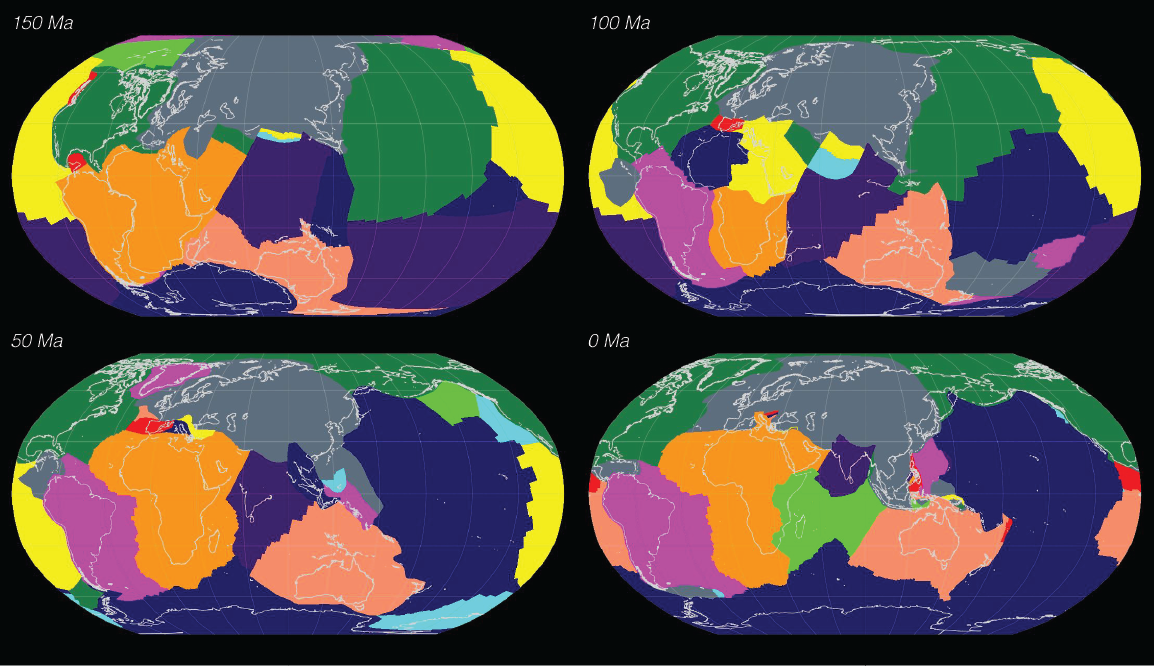
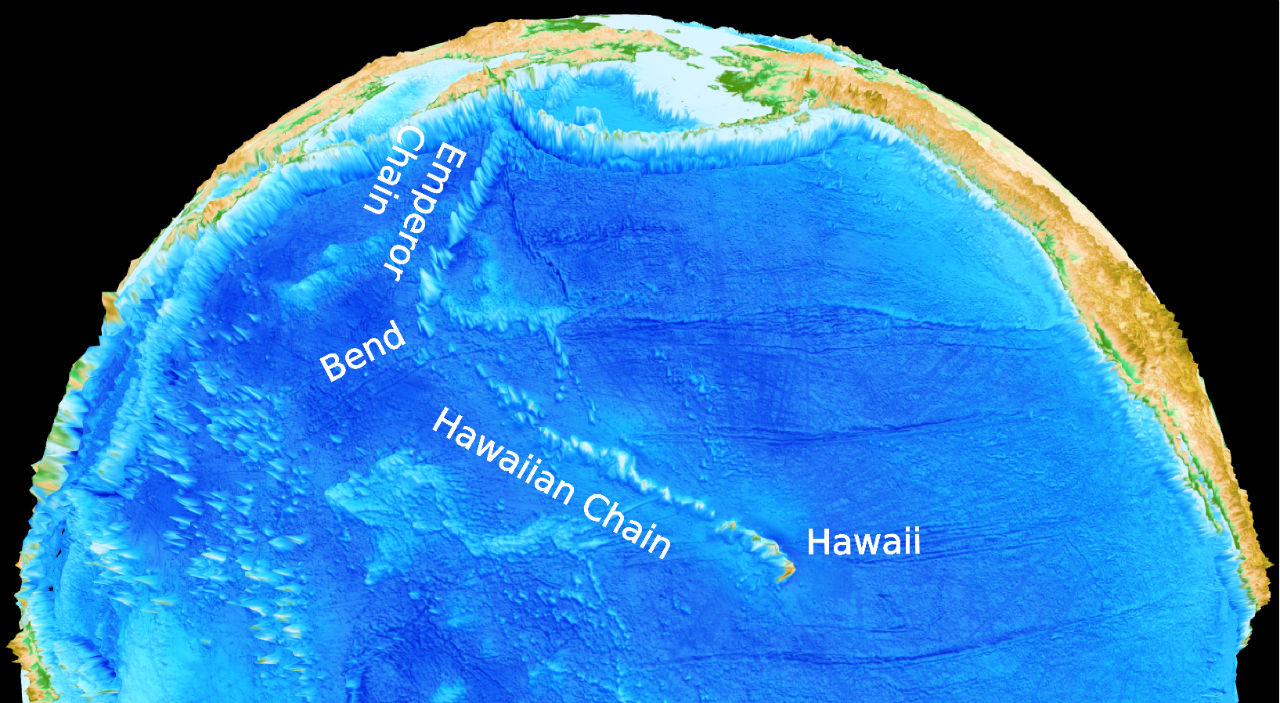
 Congratulations to Prof Dietmar Müller, Dr Nicolas Flament, Dr Kara Matthews, Dr Simon Williams, and Prof Michael Gurnis on their paper recently published in Earth and Planetary Science Letters. Their paper,
Congratulations to Prof Dietmar Müller, Dr Nicolas Flament, Dr Kara Matthews, Dr Simon Williams, and Prof Michael Gurnis on their paper recently published in Earth and Planetary Science Letters. Their paper,