 Citation
Citation
Heine, C., Yeo, L. G., & Müller, R. D. (2015). Evaluating global paleoshoreline models for the Cretaceous and Cenozoic. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, (ahead-of-print), 1-13., doi: 10.1080/08120099.2015.1018321.
Summary
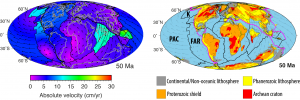
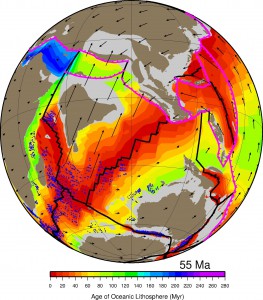
Paleoshoreline maps represent the distribution of land and sea through geologic time. These compilations provide excellent proxies for evaluating the contributions non-tectonic vertical crustal motions, such as mantle convection-driven dynamic topography, to the flooding histories of continental platforms. Until now, such data have not been available as a globally coherent compilation. Here, we present and evaluate a set of Cretaceous and Cenozoic global shoreline data extracted from two independent published global paleogeographic atlases. … Read more…