Geology: The role of surface processes in basin inversion and breakup unconformity
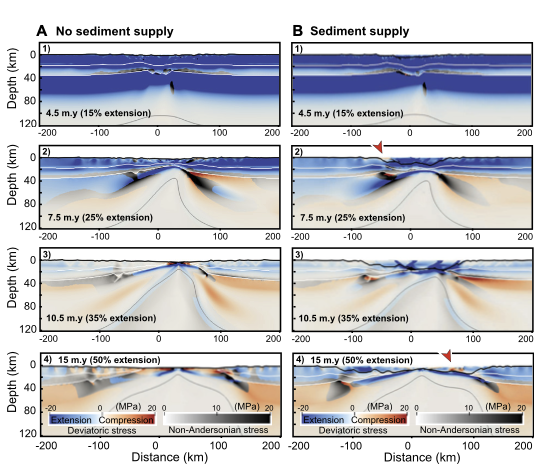
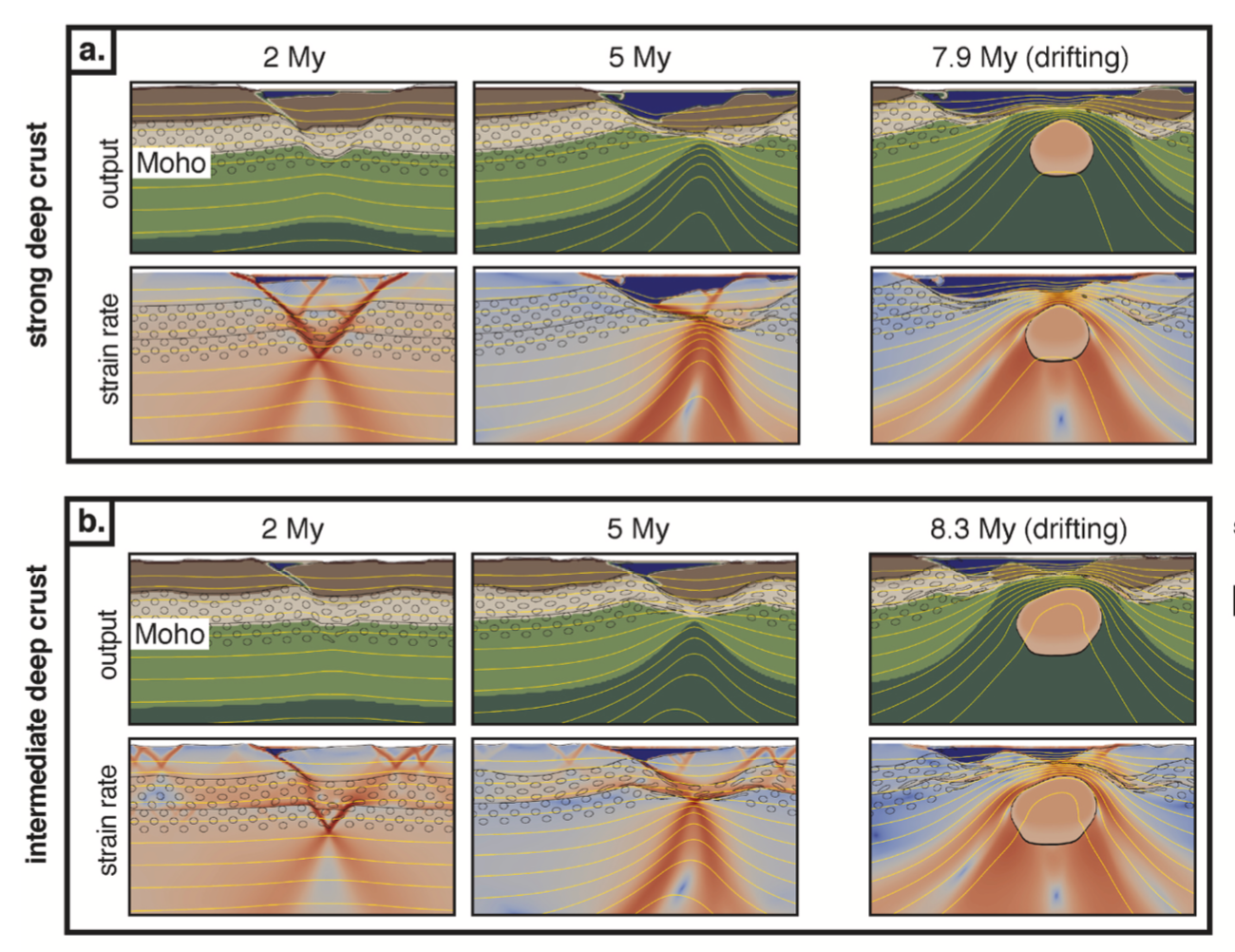
In the context of continental extension, transient compressional episodes (stress inversion) and phases of uplift (depth inversion) are commonly recorded with no corresponding change in plate motion. Changes in gravitational potential energy during the rifting process have been invoked as a possible source of compressional stresses, but their magnitude, timing, and relationship with depth inversions … Read more…