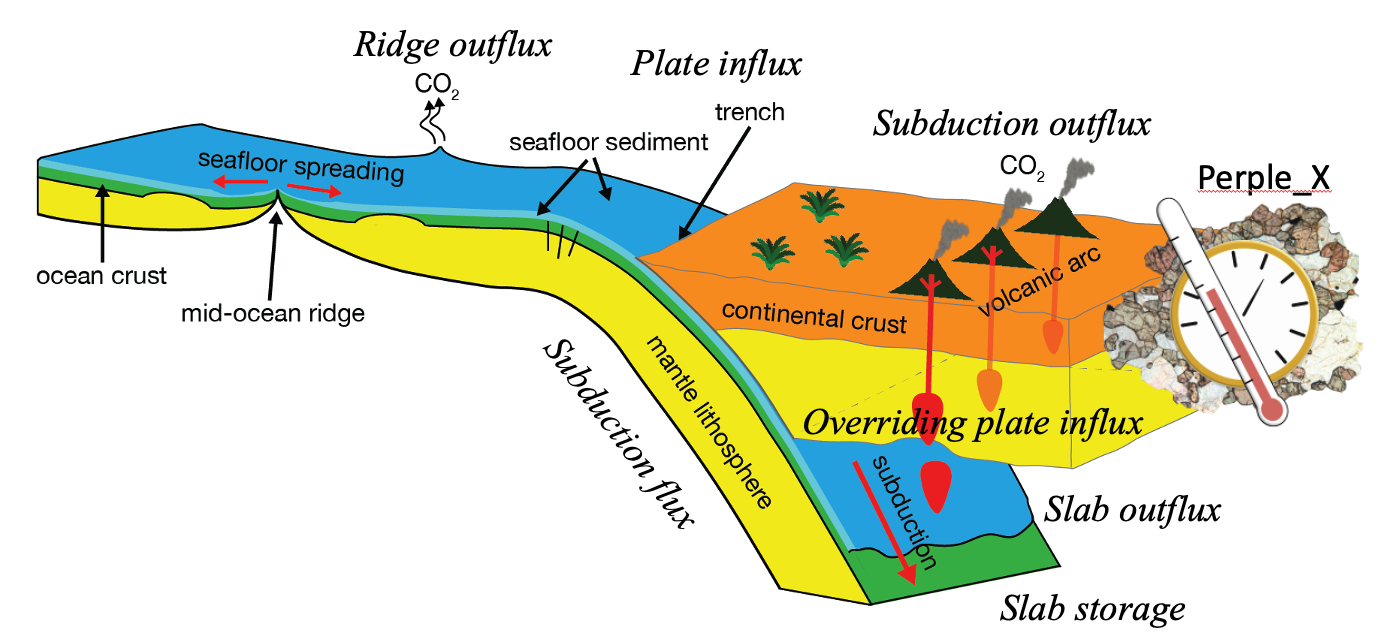
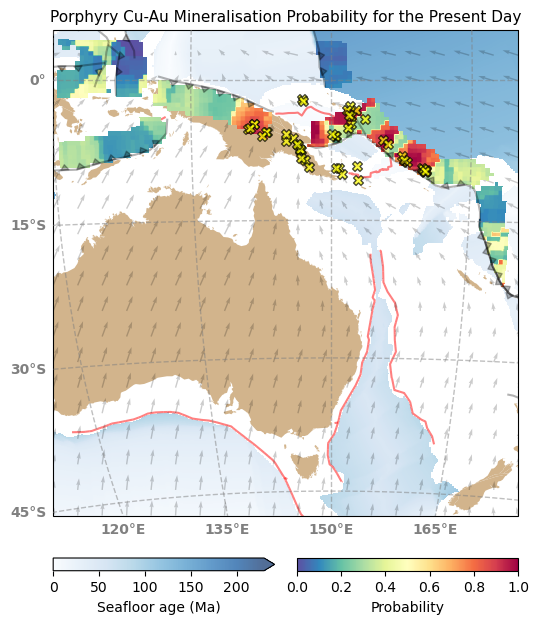
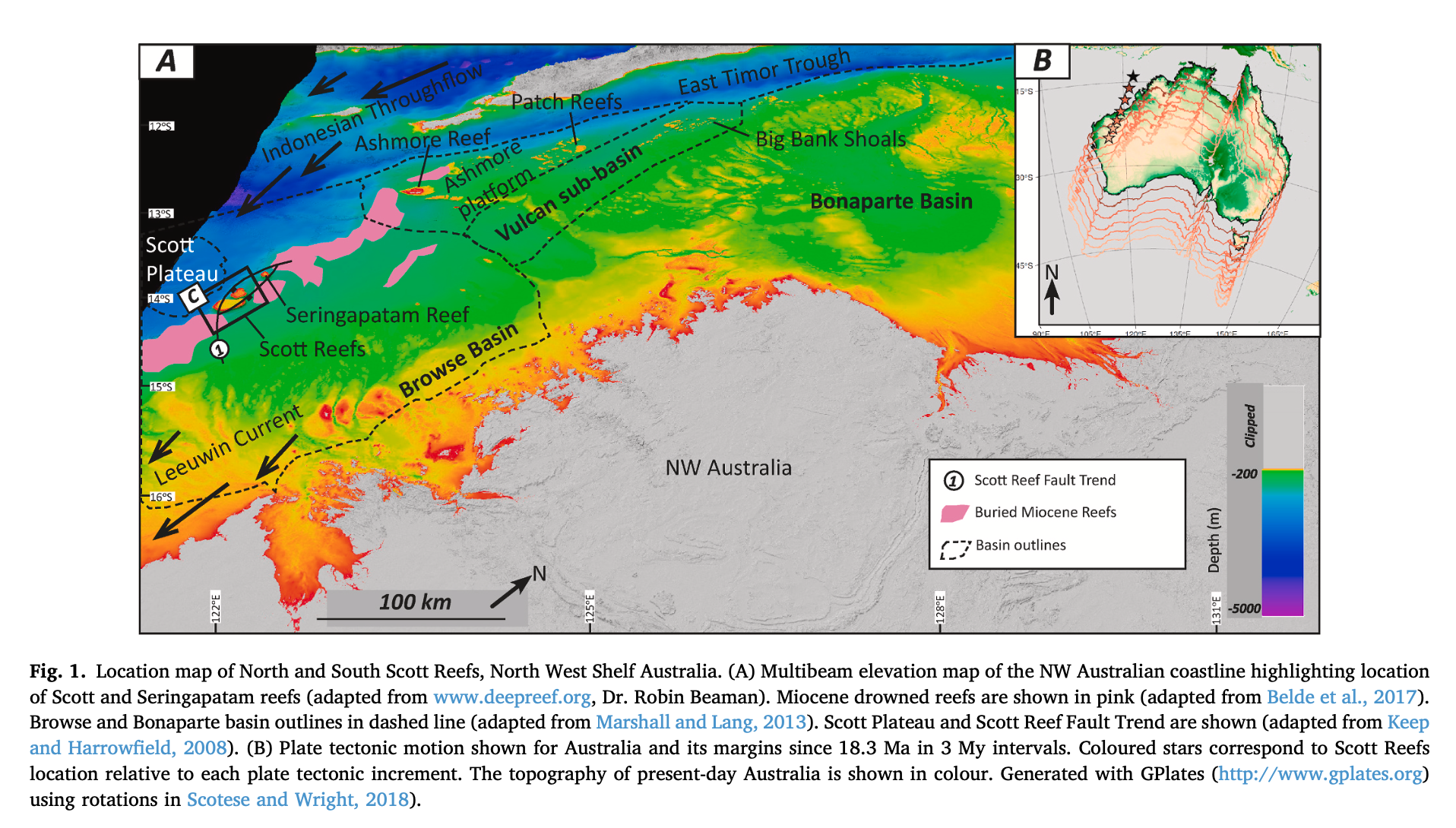
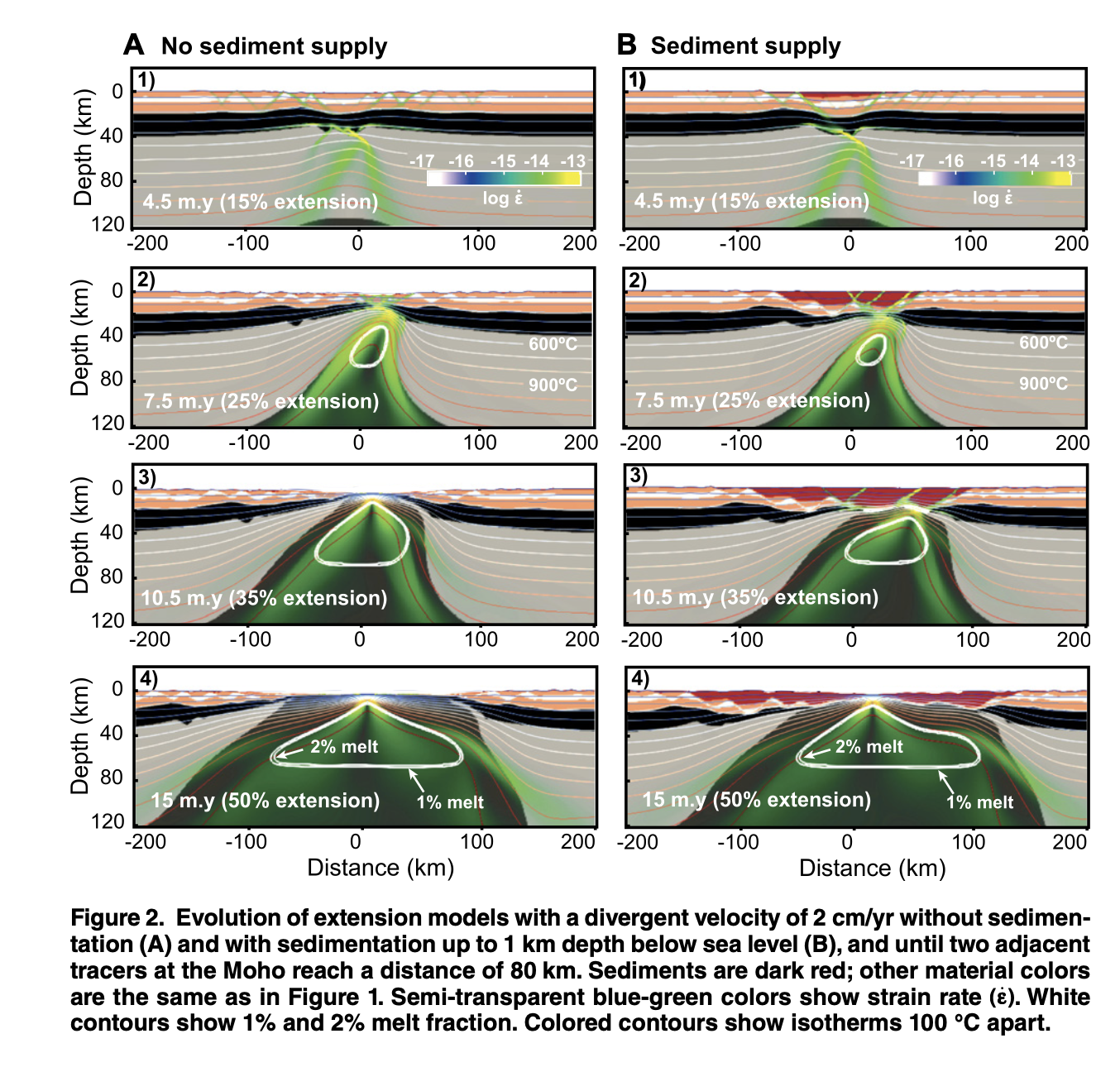
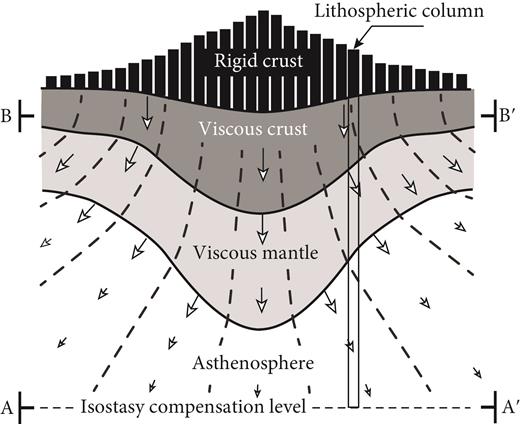
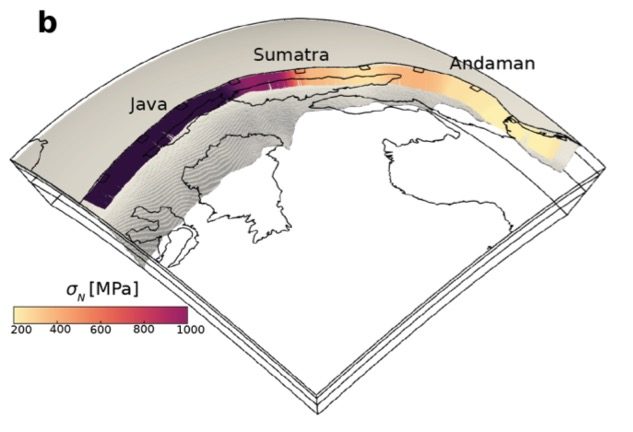
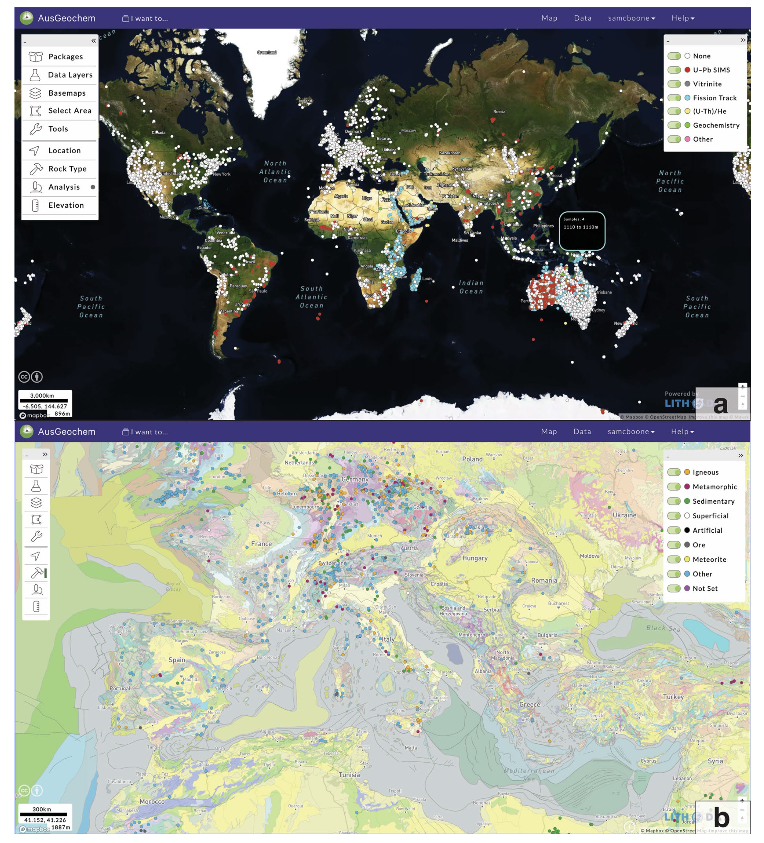
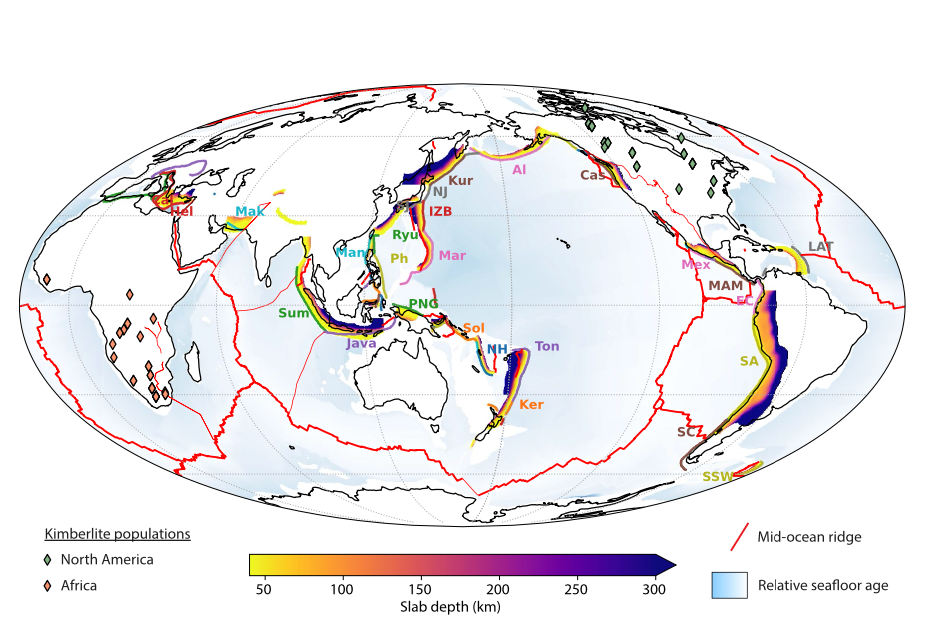
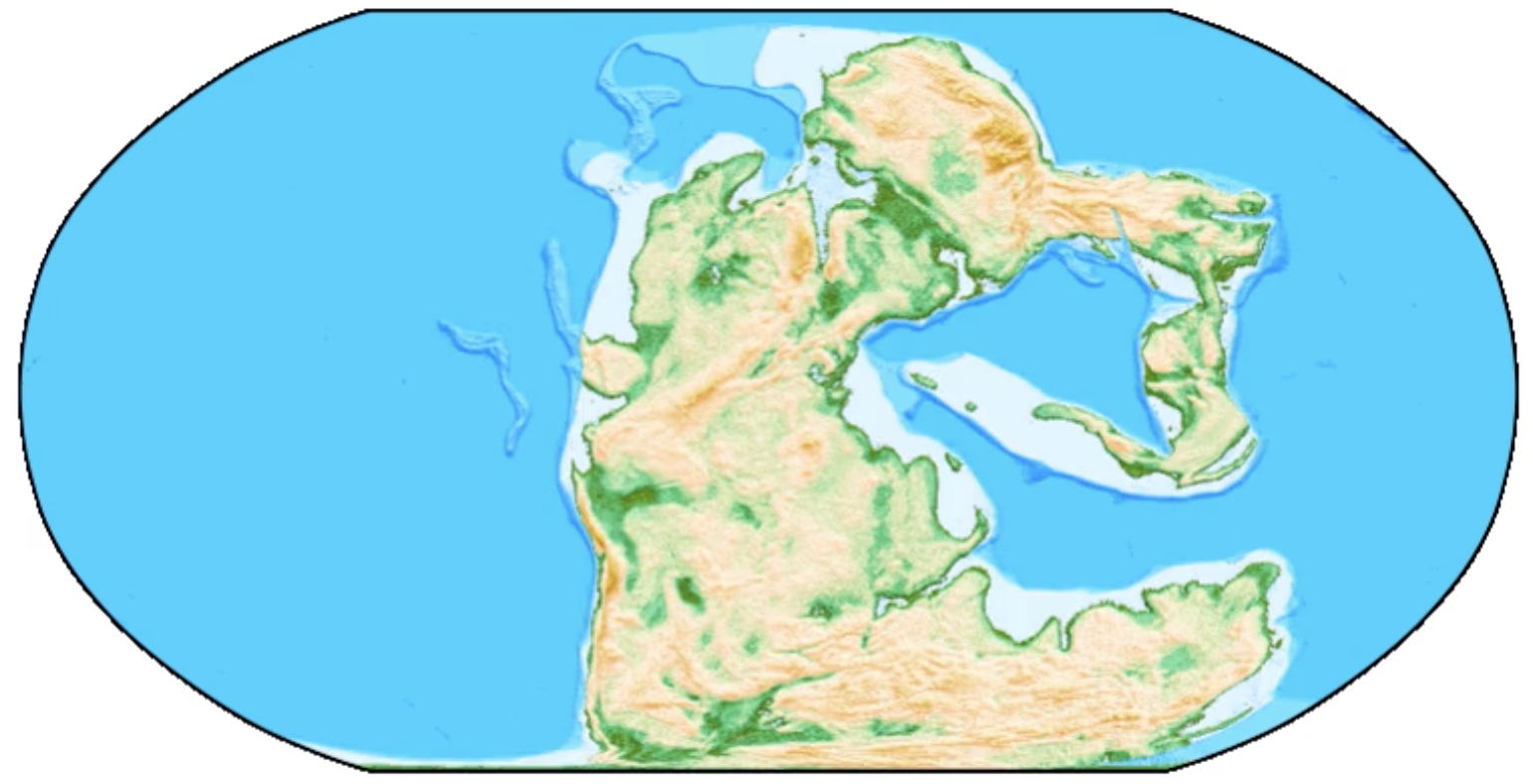
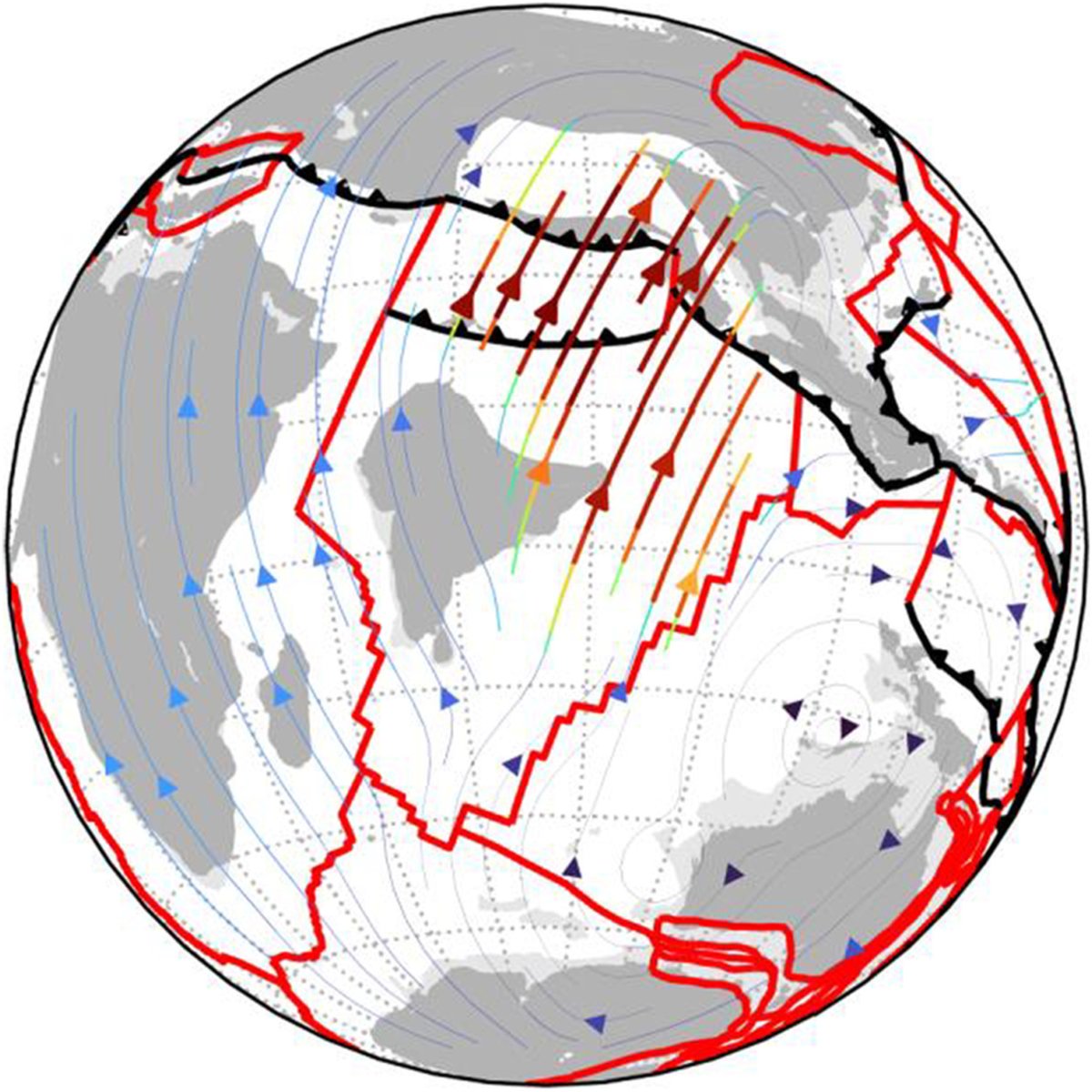
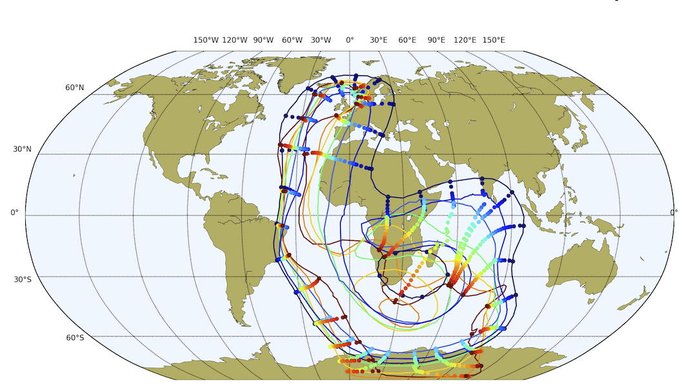
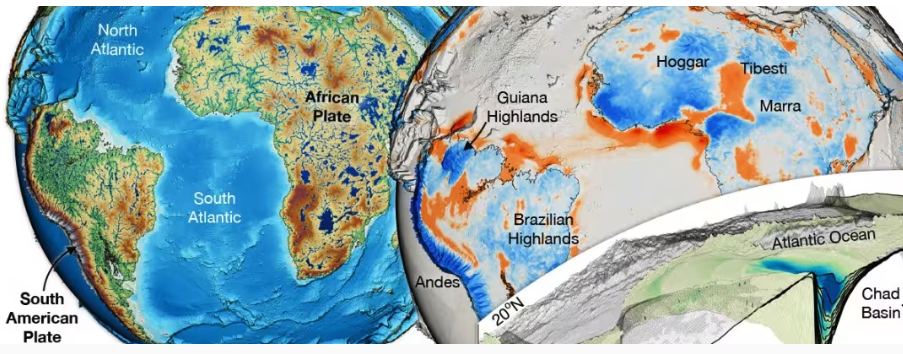
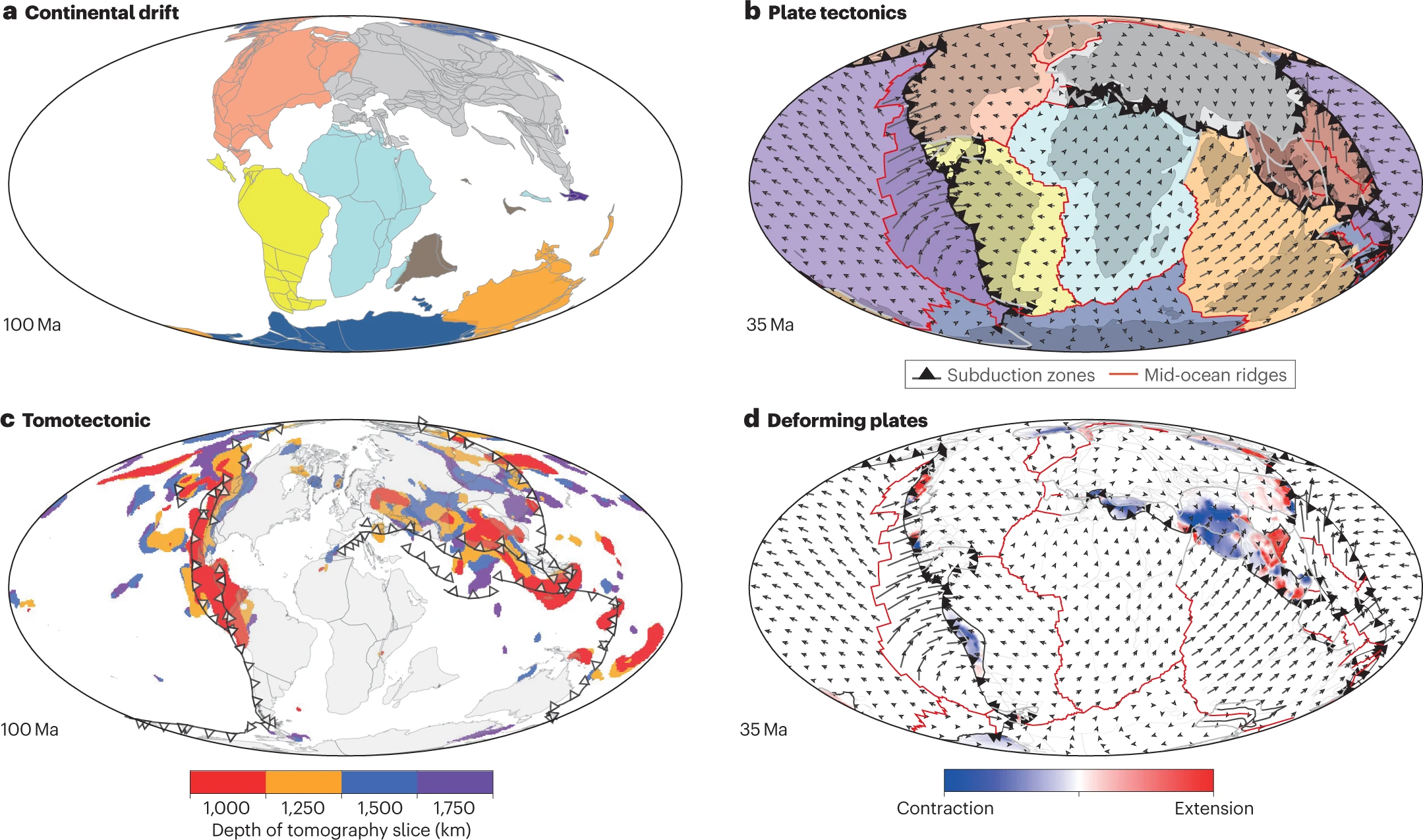
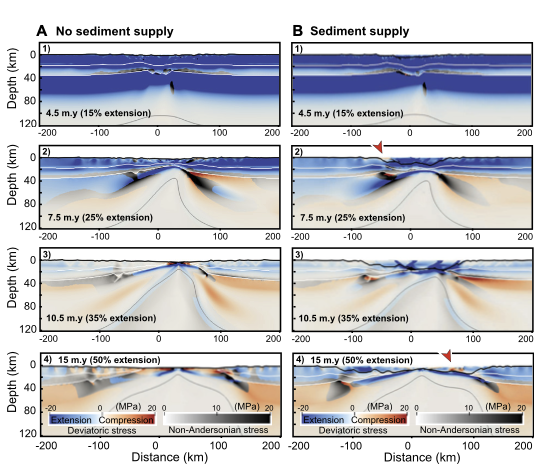
Explore Earth’s Deep Carbon Cycle with Prof. Dietmar Müller’s Tectono-Thermodynamic Modelling! In this EarthByte Seminar Series event, Dietmar talks about the “tectonic carbon conveyor belt,” its role in emitting, storing, and releasing carbon, and its impact on Earth’s climate through the ages.
More details are below:
Seminar Details:
- Date: Wednesday, 6th December 2023
- Time: 11 am – 12 pm AEDT
- Location: Geoscience Room 331 General Teaching Space and online
- Zoom Link: https://uni-sydney.zoom.us/j/86424836606 … Read more…