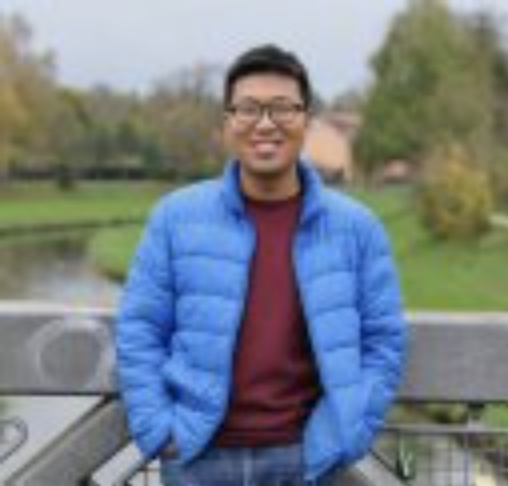
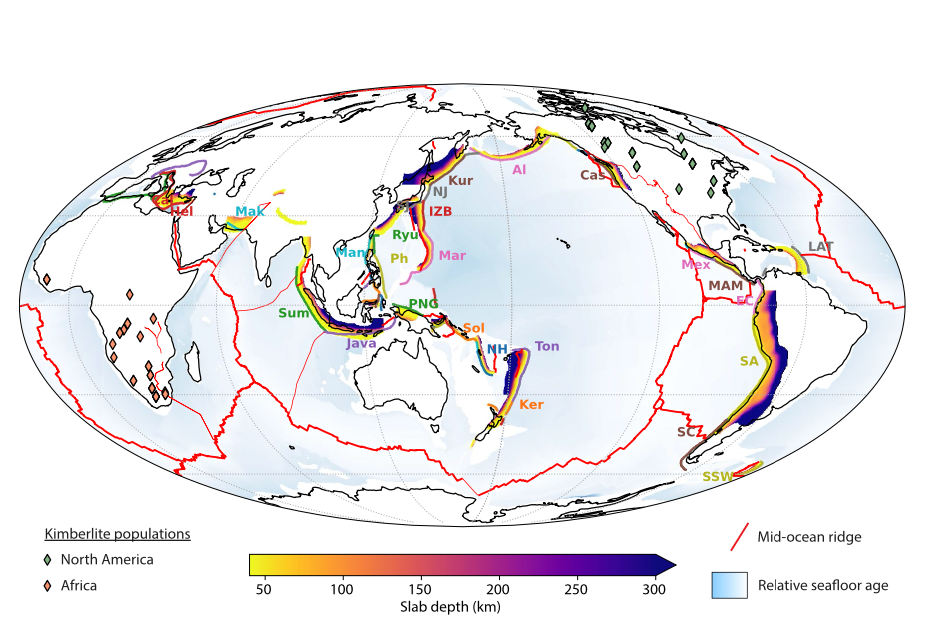
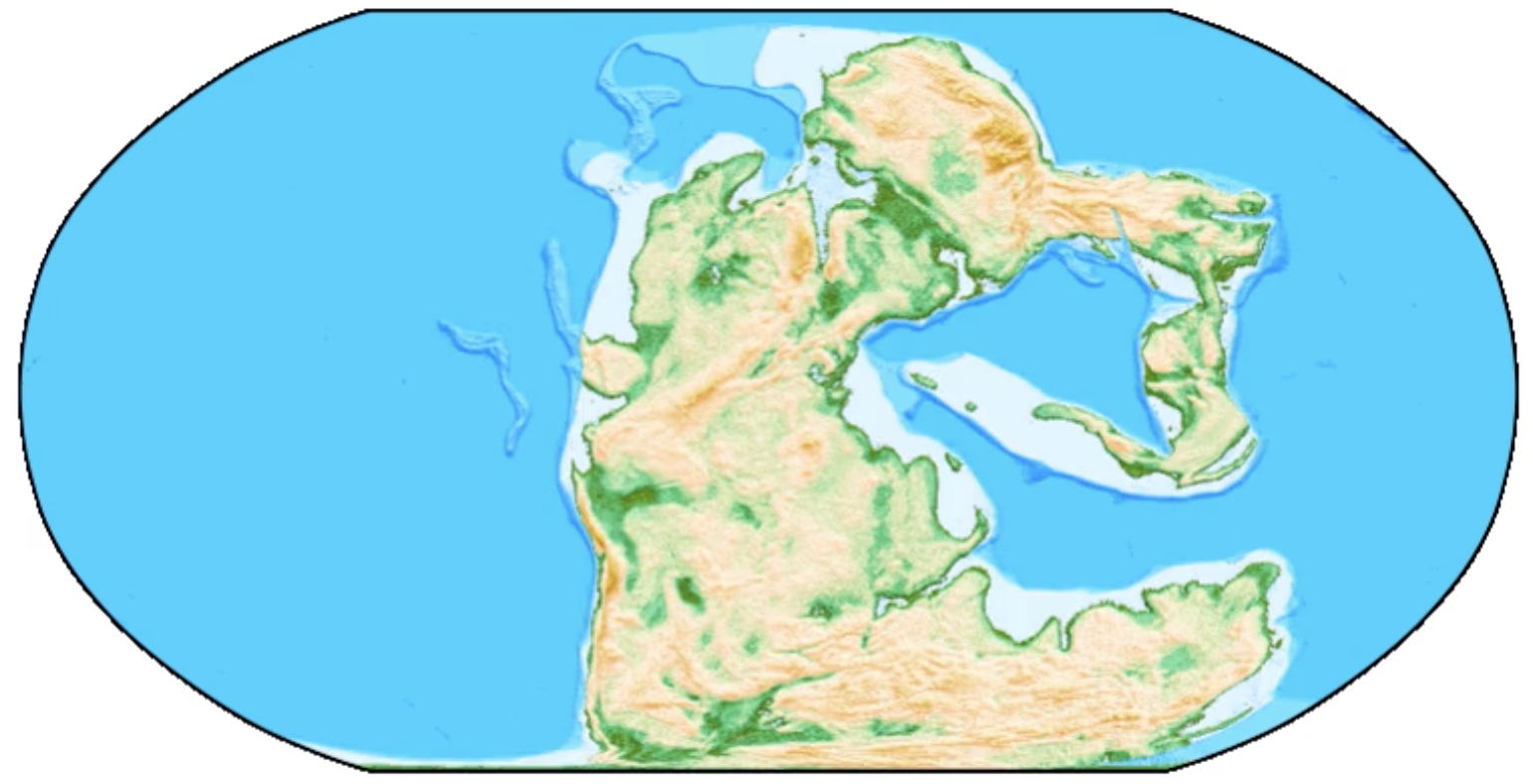
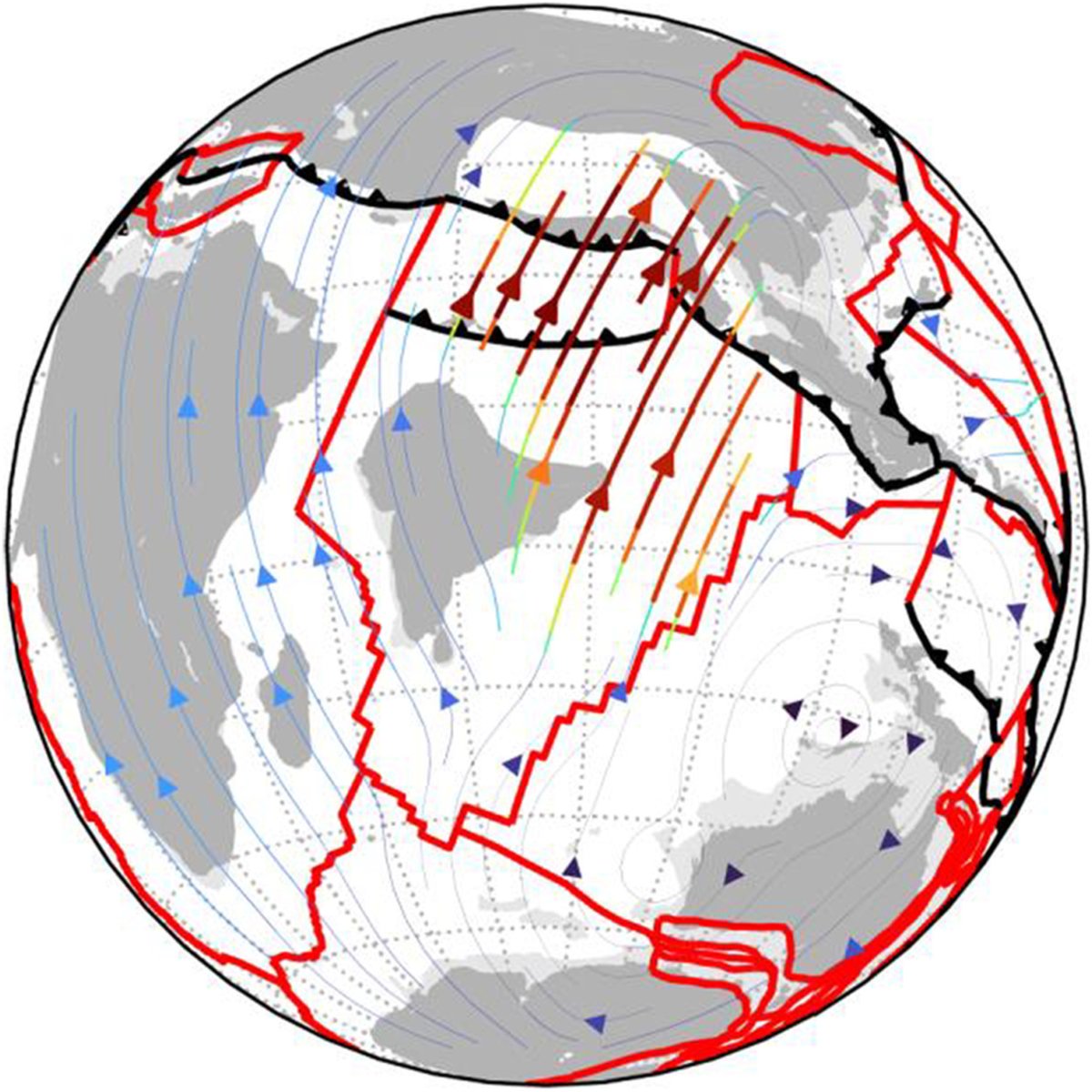
IAMG Founders Scholarship awarded to Zijing Luo
Congratulations to visiting EarthByte PhD student Zijing Luo who was awarded the IAMG Founders Scholarship. This mathematical geoscience scholarship is presented annually to an outstanding undergraduate, Masters, or Ph.D. student by the International Association of Mathematical Geosciences.