 When organic particles sink from the surface ocean to the seafloor, a small but significant proportion of atmospheric carbon is stored away. Adriana Dutkiewicz and colleagues at the University of Sydney and Data61/CSIRO have now used global data sets collected over decades combined with cutting-edge big data analysis to understand how this process depends on surface ocean environments. … Read more…
When organic particles sink from the surface ocean to the seafloor, a small but significant proportion of atmospheric carbon is stored away. Adriana Dutkiewicz and colleagues at the University of Sydney and Data61/CSIRO have now used global data sets collected over decades combined with cutting-edge big data analysis to understand how this process depends on surface ocean environments. … Read more…
Dr Adriana Dutkiewicz
Academic Staff
adriana.dutkiewicz@sydney.edu.au
Phone: +61 2 9351 5192
Madsen Building F09, Room 431School of Geosciences
The University of Sydney
Sydney, NSW 2006
Australia
View Adriana’s Sydney Uni page
See below for EarthByte content related to Adriana.
Controls on the distribution of deep-sea sediments
Author List: Dr Adriana Dutkiewicz, Dr Simon O’Callaghan, Prof Dietmar Müller Citation: Dutkiewicz, A., O’Callaghan, S., and Müller, R.D. (2016). Controls on the distribution of deep-sea sediments. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems 17 1–24. doi:10.1002/2016GC006428 Abstract: Deep-sea sediments represent the largest geological deposit on Earth and provide a record of our planet’s response to conditions at the sea surface from … Read more…
Commotion in the deep Southern Ocean
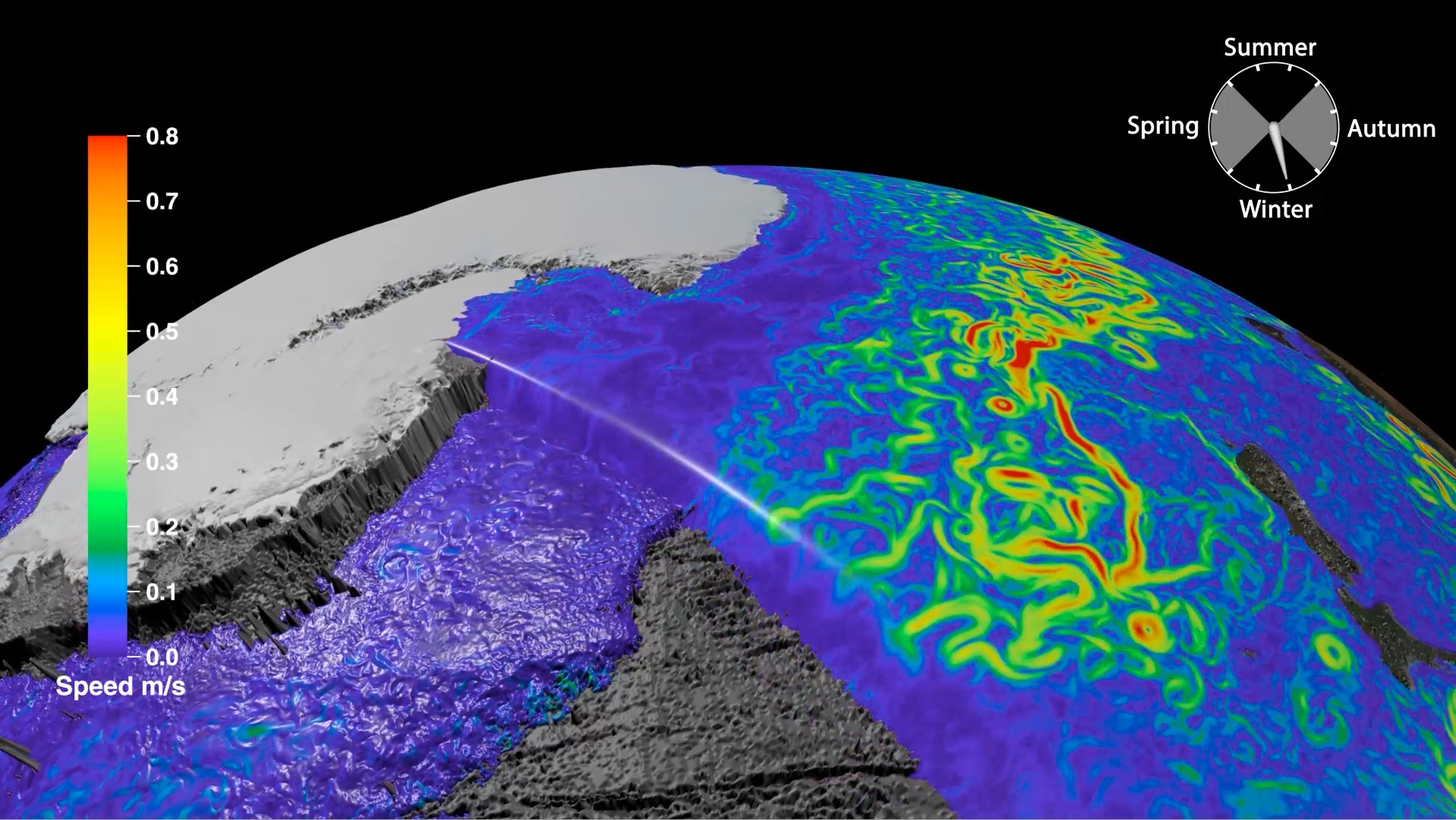 Congratulations Adriana Dutkiewicz, Dietmar Müller, Andrew Hogg, and Paul Spence for their recent paper published in Geology. Their paper, Vigorous deep-sea currents cause global anomaly in sediment accumulation in the Southern Ocean, revealed an enormous stretch of the Southern Ocean where sediments are building up at a rate that dwarfs other deep ocean locations. The work has attracted the attention of media internationally. … Read more…
Congratulations Adriana Dutkiewicz, Dietmar Müller, Andrew Hogg, and Paul Spence for their recent paper published in Geology. Their paper, Vigorous deep-sea currents cause global anomaly in sediment accumulation in the Southern Ocean, revealed an enormous stretch of the Southern Ocean where sediments are building up at a rate that dwarfs other deep ocean locations. The work has attracted the attention of media internationally. … Read more…
Vigorous deep-sea currents cause global anomaly in sediment accumulation in the Southern Ocean
Author List: Adriana Dutkiewicz, Dietmar Müller, Andy Hogg and Paul Spence. Citation: Dutkiewicz, A., Müller, R. D., Hogg, A. M. & Spence, P. (2016). Vigorous deep-sea currents cause global anomaly in sediment accumulation in the Southern Ocean. Geology, 44(8), 663–666. doi:10.1130/G38143.1 Abstract: The vigorous current systems in the Southern Ocean play a key role in regulating the Earth’s … Read more…
Commotion in the deep Southern Ocean
A team led by the University of Sydney School of Geosciences has found an 8,000-km long sediment pile-up in the middle of the Southern Ocean, making this feature unique in the world. Their study was published today in the leading international journal Geology. … Read more…
PLOS ONE – The GPlates Portal: Cloud-Based Interactive 3D Visualization of Global Geophysical and Geological Data in a Web Browser
Author List: Dietmar Müller, Xiaodong Qin, David Sandwell, Adriana Dutkiewicz, Simon Williams, Nicolas Flament, Stefan Maus, Maria Seton Citation: Müller, R. D., Qin, X., Sandwell, D. T., Dutkiewicz, A., Williams, S. E., Flament, N., Maus, S., & Seton, M. (2016). The GPlates Portal: Cloud-Based Interactive 3D Visualization of Global Geophysical and Geological Data in a Web Browser. … Read more…
GPlates Portal International Media Coverage
 The recent article on the GPlates Portal published in PLOS ONE by Prof Dietmar Müller, Xiaodong Qin, Prof David Sandwell, Dr Adriana Dutkiewicz, Dr Simon Williams, Dr Nicolas Flament, Dr Stefan Maus, and Dr Maria Seton, has received significant international media attention over the past week, featuring in articles from Australia, UK, US, India, and UAE!
The recent article on the GPlates Portal published in PLOS ONE by Prof Dietmar Müller, Xiaodong Qin, Prof David Sandwell, Dr Adriana Dutkiewicz, Dr Simon Williams, Dr Nicolas Flament, Dr Stefan Maus, and Dr Maria Seton, has received significant international media attention over the past week, featuring in articles from Australia, UK, US, India, and UAE!
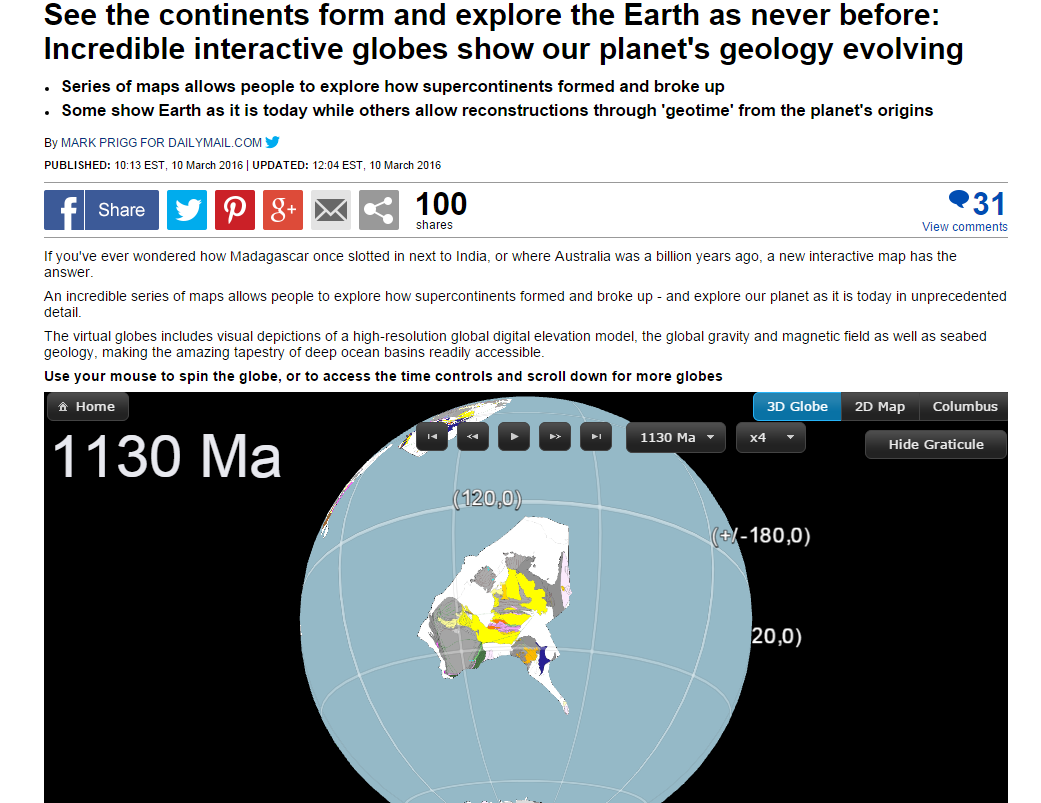
See the list of online media below, and check out the interactive globes yourself!
History and current advances in reconstructing the Earth through deep geological time
 Time machine: History and current advances in reconstructing the Earth through deep geological time – an article on Quartz by Steve LeVine. The article is a review of the development of ideas and technologies in reconstructing the Earth through deep time, aimed at understanding supercontinent assembly, breakup and dispersal, starting with Alfred Wegener. The article focusses on research activities in the context of the IGCP 648 project ‘Supercontinent Cycles and Global Geodynamics‘ led by Zheng-Xiang Li. The piece provides some historical context, and highlights the work of a number of leading scientists, postdoctoral researchers and PhD students currently involved in this work. … Read more…
Time machine: History and current advances in reconstructing the Earth through deep geological time – an article on Quartz by Steve LeVine. The article is a review of the development of ideas and technologies in reconstructing the Earth through deep time, aimed at understanding supercontinent assembly, breakup and dispersal, starting with Alfred Wegener. The article focusses on research activities in the context of the IGCP 648 project ‘Supercontinent Cycles and Global Geodynamics‘ led by Zheng-Xiang Li. The piece provides some historical context, and highlights the work of a number of leading scientists, postdoctoral researchers and PhD students currently involved in this work. … Read more…
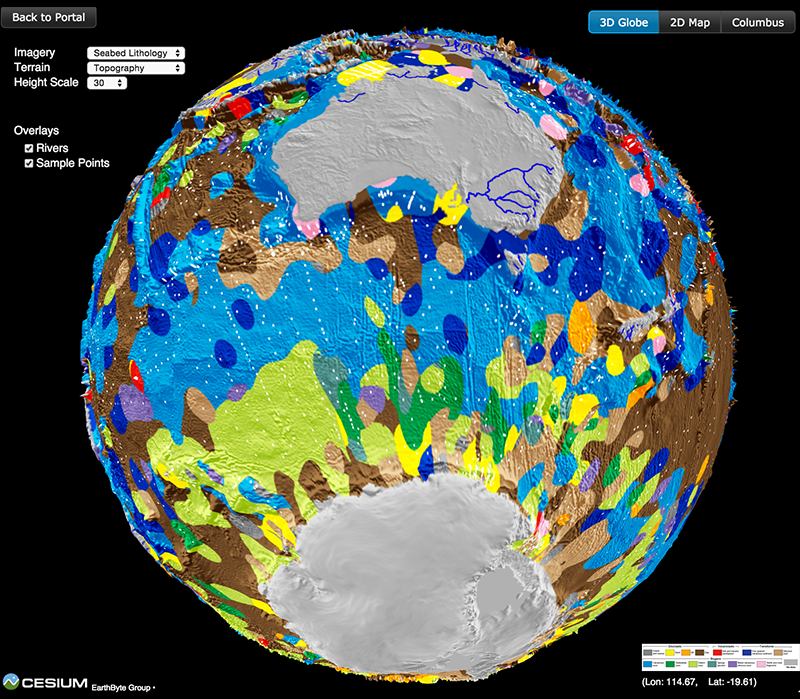
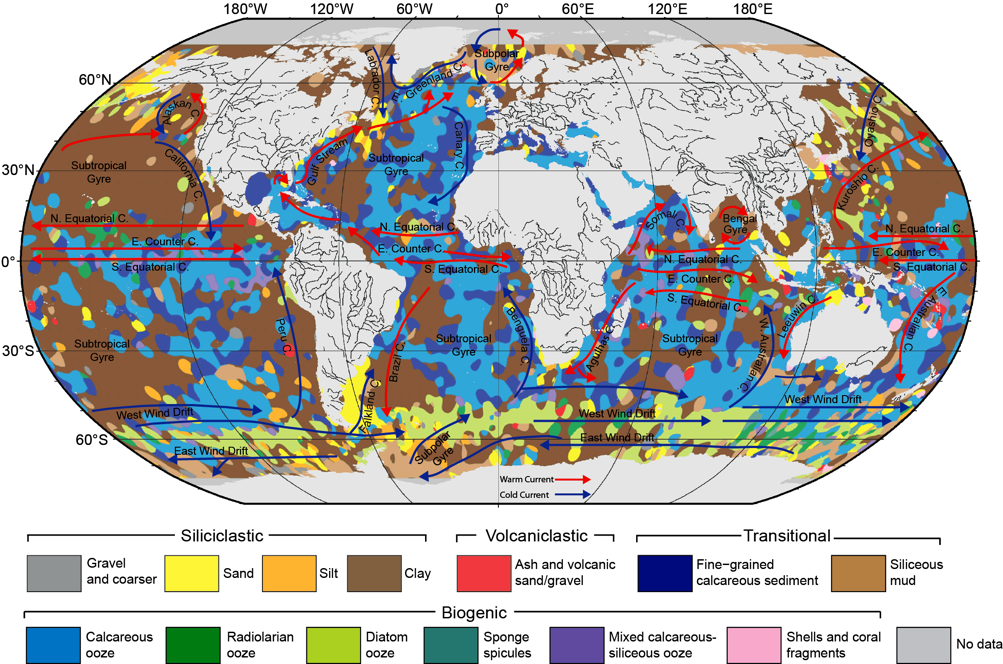
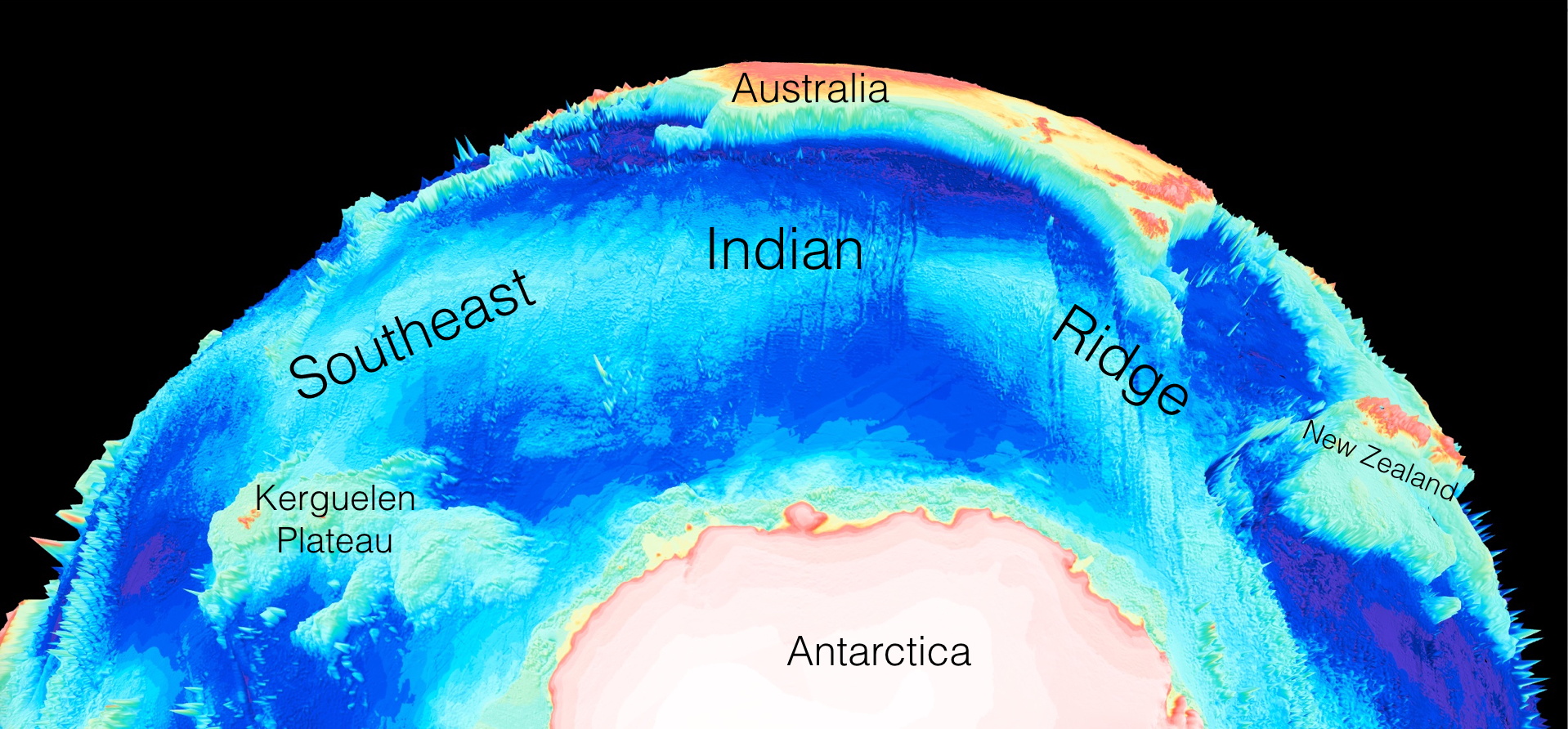
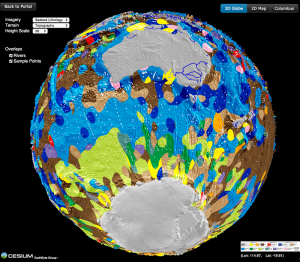
Seafloor lithology of the ocean basins
 Citation
Citation
Dutkiewicz, A., Müller, R. D., O’Callaghan, S., & Jónasson, H. (2015). Census of seafloor sediments in the world’s ocean. Geology, G36883-1. doi: 10.1130/G36883.1.
Abstract
Knowing the patterns of distribution of sediments in the global ocean is critical for understanding biogeochemical cycles and how deep-sea deposits respond to environmental change at the sea surface. We present the first digital map of seafloor lithologies based on descriptions of nearly 14,500 samples from original cruise reports, interpolated using a support vector machine algorithm. We show that sediment distribution is more complex, with significant deviations from earlier hand-drawn maps, and that major lithologies occur in drastically different proportions globally. … Read more…
Homeward Bound… Big Data Reveals Geology of World's Ocean Floor
The 2015 Ocean Innovation (OI) conference takes place in St. John’s, Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada during October and focuses on “mapping our oceans.” For each OI conference, a special issue of The Journal of Ocean Technology (JOT) that complements the conference’s theme is released. A series of essays, peer review technical papers, and columns are included and … Read more…
Homeward Bound… Big Data Reveals Geology of World’s Ocean Floor
The 2015 Ocean Innovation (OI) conference takes place in St. John’s, Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada during October and focuses on “mapping our oceans.” For each OI conference, a special issue of The Journal of Ocean Technology (JOT) that complements the conference’s theme is released. A series of essays, peer review technical papers, and columns are included and … Read more…
Ocean sediment map makes world news
 The recently-published ocean sediment map made by Dr Adriana Dutkiewicz and colleagues has taken the world’s media by storm. It’s been reported online and in press, from Australia to Cuba, Hungary and many other countries! See the updated list of media items below, and check out the link to the interactive 3D globe with the ocean sediments map.
The recently-published ocean sediment map made by Dr Adriana Dutkiewicz and colleagues has taken the world’s media by storm. It’s been reported online and in press, from Australia to Cuba, Hungary and many other countries! See the updated list of media items below, and check out the link to the interactive 3D globe with the ocean sediments map.
Countries where the story has been covered so far:
Australia, UK, USA, India, Italy, Germany, Spain, Hungary, Austria, Cuba, Costa Rica and Peru.
Radio Interviews
ABC 774 Melbourne
World’s first digital seafloor map reveals ‘paradise’ – ABC Rural Radio
ABC 702 Sydney
BBC Radio 5 Live’s “Up All Night”
It took more than a year of research and sifting through thousands of samples to generate the world’s first digital map of the seafloor – ABC Country Radio (Interview at 41:10) … Read more…
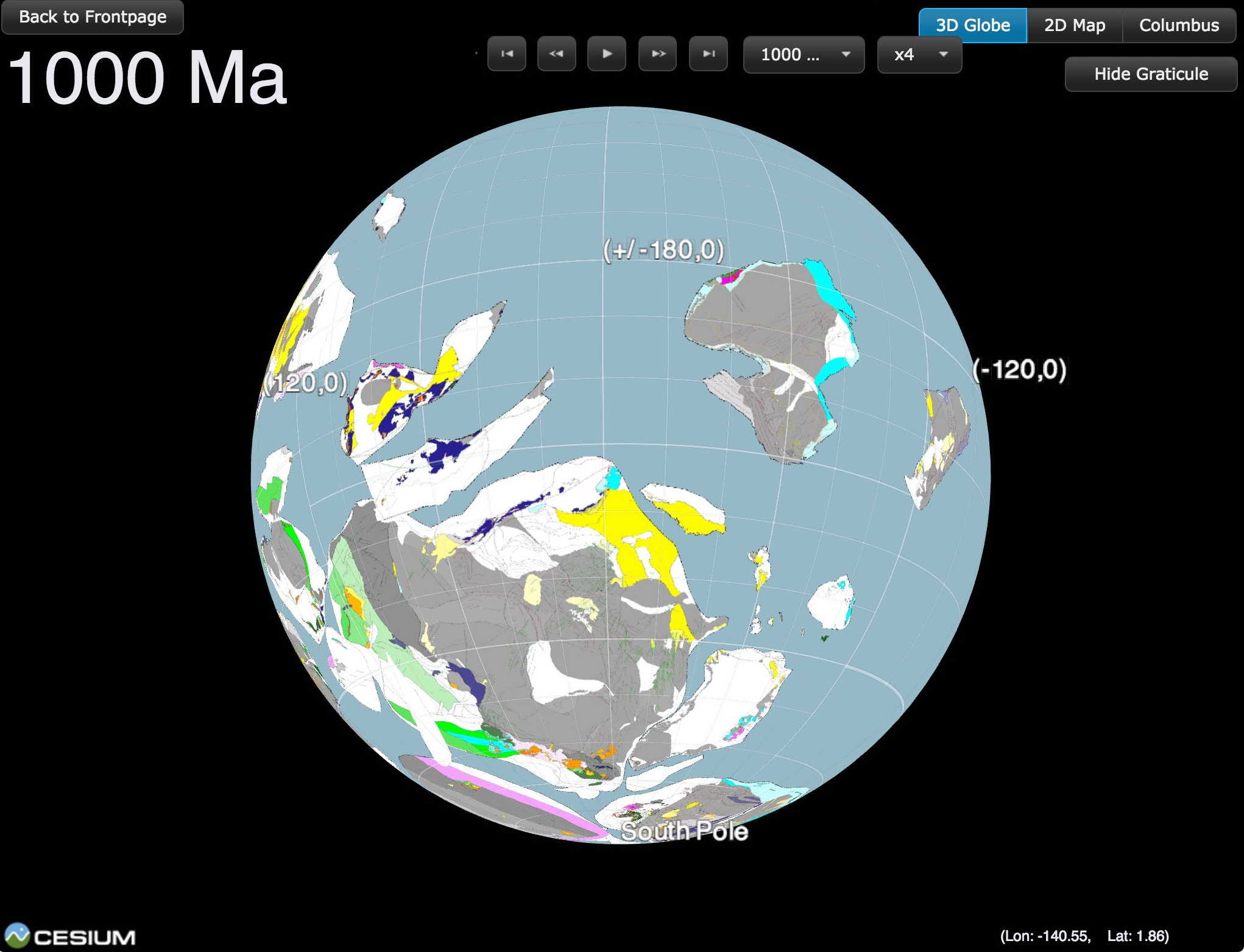
Virtual seafloor geology globe spinning North-South
This spinning virtual seafloor geology globe is composed of a set of screen captures of an interactive digital globe portraying the distribution of different seafloor sediments available at the Gplates Portal.Citation Dutkiewicz, A., Müller, R. D., O’Callaghan, S., & Jónasson, H. (2015). Census of seafloor sediments in the world’s ocean. Geology, G36883-1. doi: 10.1130/G36883.1.Download paper … Read more…
Virtual seafloor geology globe spinning East-West
This spinning virtual seafloor geology globe is composed of a set of screen captures of an interactive digital globe portraying the distribution of different seafloor sediments available at the Gplates Portal.Citation Dutkiewicz, A., Müller, R. D., O’Callaghan, S., & Jónasson, H. (2015). Census of seafloor sediments in the world’s ocean. Geology, G36883-1. doi: 10.1130/G36883.1.Download paper … Read more…
Big data reveals geology of world’s ocean floor
 A team led by the University of Sydney School of Geosciences has created the first digital globe of seafloor sediments.
A team led by the University of Sydney School of Geosciences has created the first digital globe of seafloor sediments.
Ocean sediments cover 70% of our planet’s surface, forming the substrate for the largest ecosystem on Earth and its largest carbon reservoir – but the most recent map of seafloor geology was drawn by hand over 40 years ago, at the dawn of modern ocean exploration.
That’s about to change. In a gargantuan effort Adriana Dutkiewicz and her colleagues carefully analysed and categorised 15,000 seafloor sediment samples to reveal the nature of sedimentary blankets over ocean ridges, seamounts and the vast abyssal plains. She teamed up with big data experts to find the best way to use modern computer algorithms to turn the vast sea of point observations into a continuous digital map. … Read more…
Big Data Knowledge Discovery
Big Data Knowledge Discovery is an interdisciplinary research initiative that focuses on the scientific challenges and opportunities presented by the use of the new techniques of data science applied in the natural sciences. This research initiative brings together world class discipline leaders in the data-intensive sciences of Geo Sciences, Life Sciences and Physical Sciences with … Read more…
Geology – Census of seafloor sediments in the world's ocean
Dutkiewicz, A., Müller, R. D., O’Callaghan, S., & Jónasson, H. (2015). Census of seafloor sediments in the world’s ocean. Geology, G36883-1. doi: 10.1130/G36883.1. Census of seafloor sediments in the world’s ocean
Geology – Census of seafloor sediments in the world’s ocean
Dutkiewicz, A., Müller, R. D., O’Callaghan, S., & Jónasson, H. (2015). Census of seafloor sediments in the world’s ocean. Geology, G36883-1. doi: 10.1130/G36883.1. Census of seafloor sediments in the world’s ocean
Gondwana Research – Origin of silica and fingerprinting of Australian sedimentary opals
Dutkiewicz, A., Landgrebe, T. C., & Rey, P. F. (2015). Origin of silica and fingerprinting of Australian sedimentary opals. Gondwana Research, 27(2), 786-795. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.10.013. Origin of silica and fingerprinting of Australian sedimentary opals
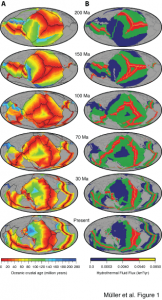
Seawater chemistry driven by supercontinent assembly, breakup and dispersal, Müller et al. (2013)
 Citation
Citation
Müller, R. D., Dutkiewicz, A., Seton, M. and Gaina, C. (2013). Seawater chemistry driven by supercontinent assembly, break-up and dispersal Geology. doi 10.1130/G34405.1.
Summary
Global oceans are known to have alternated between aragonite and calcite seas. These oscillations reflect changes in the Mg/Ca ratio of seawater, which control biomineralisation and the composition of marine carbonates and are thought to be caused by the time dependence of crustal accretion at mid-ocean ridge crests and associated high temperature mid-ocean ridge brine flux. Here we use global ocean basin reconstructions to demonstrate that these fluctuations are instead caused by the gradual growth and destruction of mid-ocean ridges and their relatively cool flanks during long-term tectonic cycles thus linking ocean chemistry to off-ridge low temperature hydrothermal flux. Early Jurassic aragonite seas were a consequence of supercontinent stability and minima in mid-ocean ridge length and basalt alteration. The break-up of Pangaea led to a gradual doubling in ridge length and a 50% increase in hydrothermal flux mainly through an enormous increase in ridge flank area, leading to enhanced alteration of basalt, lowered seawater Mg/Ca ratios and marine hypercalcification from 140 to 35 Ma. … Read more…
Opal exploration research recognised as outstanding highlight
Recent EarthByte research on opal exploration was recognised as an outstanding highlight and reflects the work of many of the group including, Andrew Merdith, Tom Landgrebe, Adriana Dutkiewicz and Patrice Rey. Congratulations to all of the contributors to the project and specifically to John Cannon and Michael Chin, the GPlates developers!
Geology – Seawater chemistry driven by supercontinent assembly, breakup, and dispersal
Müller, R. D., Dutkiewicz, A., Seton, M., & Gaina, C. (2013). Seawater chemistry driven by supercontinent assembly, breakup, and dispersal. Geology, 41(8), 907-910. doi: 10.1130/G34405.1. Seawater chemistry driven by supercontinent assembly, breakup, and dispersal
Australian Journal of Earth Sciences – Towards a predictive model for opal exploration using a spatio-temporal data mining approach
Merdith, A. S., Landgrebe, T. C., Dutkiewicz, A., & Müller, R. D. (2013). Towards a predictive model for opal exploration using a spatio-temporal data mining approach. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 60(2), 217-229. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/08120099.2012.754793. Towards a predictive model for opal exploration using a spatio-temporal data mining approach Supplementary data
From data mining to opal mining
 Documents
Documents
AJES Paper
CG Paper
Opal is Australia’s national gemstone, however most significant opal discoveries were made in the early 1900’s – more than 100 years ago – until recently. Currently there is no formal exploration model for opal, meaning there are no widely accepted concepts or methodologies available to suggest where new opal fields may be found. … Read more…
Computers & Geoscience – Relationships between palaeogeography and opal occurrence in Australia: a data-mining approach
Landgrebe, T. C. W., Merdith, A., Dutkiewicz, A., & Müller, R. D. (2013). Relationships between palaeogeography and opal occurrence in Australia: A data-mining approach. Computers & Geosciences, 56, 76-82. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2013.02.002. Download the paper – pdf
Computers & Geoscience – Relationships between palaeogeography and opal occurrence in Australia: a data-mining approach
Landgrebe, T. C. W., Merdith, A., Dutkiewicz, A., & Müller, R. D. (2013). Relationships between palaeogeography and opal occurrence in Australia: A data-mining approach. Computers & Geosciences, 56, 76-82. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2013.02.002. Download the paper – pdf
EarthByte to attend AGU 2011
EarthByte group members Dietmar Müller, Adriana Dutkiewicz, Nicolas Flament, Leonardo Quevedo, Maria Seton, Simon Williams, Nathaniel Butterworth, Kayla Maloney and Kara Matthews are attending the AGU Fall Meeting 2011 in San Francisco, USA from 5-9 December, 2011. Click here for more details about the AGU Fall Meeting
Adriana Dutkiewicz awarded Dorothy Hill Award and the CSIRO Medal
Congratulations to Adriana Dutkiewicz who was awarded the Dorothy Hill Award from the Australian Academy of Science and the CSIRO Medal for Scientific Achievement (group award). Well done Adriana!
Chemistry of the Archaean Ocean and its impact on Earth’s early atmosphere and ecosystems
ARC Linkage Project Project Participants Dr Patrice Rey Dr P. Philippot Dr Adriana Dutkiewicz Dr Craig Marshall Dr M. J. Van Kranendonk Publications Project Contact Dr Patrice Rey
Chemistry of the Archaean Ocean and its impact on Earth's early atmosphere and ecosystems
ARC Linkage Project Project Participants Dr Patrice Rey Dr P. Philippot Dr Adriana Dutkiewicz Dr Craig Marshall Dr M. J. Van Kranendonk Publications Project Contact Dr Patrice Rey